eINDUSTRIFY is the industrial B2B marketplace that connects leading distributors with global customers.

Cutting-Edge Technology
ERP Enablement, Marketing Provision & Support, Shipment APIs & Analytics

Punch-Out Model
Achieve ROI without capex. Empowers both customers and providers

The Right Partner
Provides businesses with the tools they need to achieve growth & revenue goals

The Right Reach
A competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving world of B2B ecommerce.
Follow our streamlined and efficient registration process for seamless user onboarding, ensuring swift access to services with minimal hassle.

Start your B2B e-commerce journey by filling out our user-friendly application form. Our dedicated category experts will carefully evaluate your submission. If your products align with our platform, our team will reach out to you directly.

Once your application is approved and progress to the final setup phase in our portal. Work closely with your designated eINDUSTRIFY buyer to orchestrate the launch of your products.

We meticulously package and dispatch your products to customers. We also work with drop-ship partners if it is a good fit for both.
Our platform offers a wide range of features and services that are tailored to meet the needs of vendors
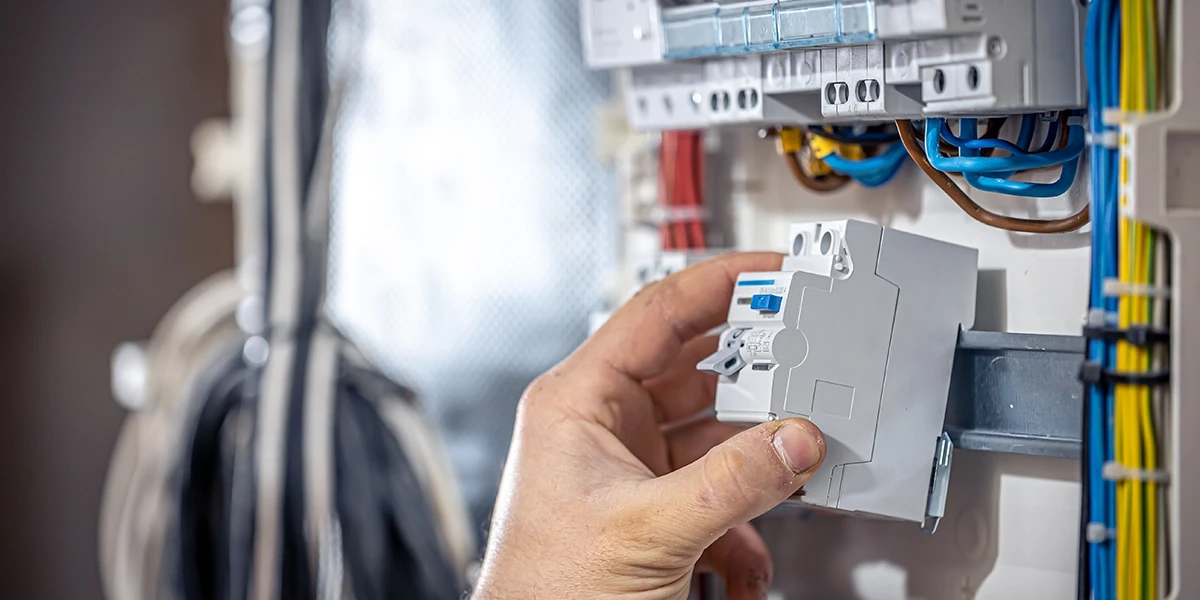

In most power generation plants and heavy industrial facilities, a single wrong trip can turn a local fault into a full-site blackout. Industrial circuit breakers are devices that decide whether a fault stays local or takes down the generator, transformers, and critical loads. They protect people from arc flash, protect high-value assets, and protect uptime by preventing nuisance trips and uncontrolled failures. This article walks through the main breaker types, how they operate in real plants, what can go wrong, and how to choose and coordinate them for safety and reliability.When One Fault Trips the Whole PlantPicture a fault on a low-voltage motor feeder in a power plant. The downstream breaker should clear it, but the wrong industrial breaker trips upstream, destabilizes the system, and the generators trip offline. During a 2016 Jamaican system event, the intended breakers failed to clear the fault, backup protection responded too slowly, and all online generators tripped within seconds, causing a grid collapse. DNV reports similar patterns in heavy industry, where breaker or protection failures in oil and gas and refineries have led to production-wide blackouts and multi-million-dollar losses. Industrial circuit breakers and the breaker panel architecture around them are therefore a primary safety system for: Personnel safety around live equipment and arc flash Asset protection for generators, transformers, cables, and motors Uptime is achieved by preventing a single fault from dropping the entire plant down.What Makes Industrial Circuit Breakers Different in Power GenerationIndustrial circuit breakers in power plants and heavy industry handle higher fault levels, harsher environmental conditions, and more demanding duty cycles than domestic devices. They are expected to clear large short-circuit currents quickly while still riding through high inrush currents and frequent switching of large motors and transformers. Three safety lenses define their job: Personnel safety: Arc flash in switchgear and breaker panels can reach temperatures above 35,000°F and cause around 30,000 incidents, 7,000 burn injuries, 2,000 hospitalizations, and roughly 400 deaths per year in the US Asset protection: Correctly chosen industrial breakers limit let-through energy to prevent catastrophic damage to generators, transformers, and cables during faults Uptime and nuisance trip avoidance: False tripping, where a breaker opens when it should not, is the single most common failure mode, accounting for 42 percent of breaker failures in distribution systems. In the background, engineers use standards as guardrails: IEC 60947-2 for low-voltage industrial circuit breakers; IEC 62271-100 for high-voltage breaker switchgear; IEC/IEEE 62271-37-013 for generator breakers; and NFPA 70E for arc-flash and electrical safety practices. Types of Industrial Circuit Breakers Used in Power Generation and Heavy IndustryDifferent parts of a power generation or heavy industrial system call for different breaker technologies at different voltage and current levels. A designer or maintenance lead needs a precise mapping of breaker types to their duties in the plant.Mini Circuit Breaker (MCB) in Control and Auxiliary CircuitsA mini circuit breaker protects small branch circuits in industrial environments, such as control circuits, instrument loops, and local lighting. Typical ratings range from about 100–125 A, with fixed trip characteristics determined by B, C, or D curves under IEC 60898- 1. In a power plant, a mini circuit breaker is appropriate where fault currents are relatively modest, and loads are small, but where reliable, resettable protection is still essential for safety and continuity of control systems. Molded Case Breaker (MCCB) as the Industrial WorkhorseA molded case breaker covers a wide range of currents, typically 10 A to 1,600 A or more, in a compact, insulated housing that withstands dust, moisture, and mechanical stress. In power generation and heavy industry, molded case breakers protect feeders, motor control centers, and large motors that drive pumps, fans, and process equipment. Most industrial molded case breakers include both: A thermal element for overload protection over time A magnetic element for fast short-circuit protection. Adjustable thermal and magnetic settings make the molded case breaker central to selective coordination and nuisance trip reduction. Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) in Main LV SwitchgearAn air circuit breaker serves as the main incoming, tie, or bus coupler breaker in low-voltage switchgear, typically handling currents from 800 A to 6,300 A. It uses air as the arc quenching medium and relies on robust arc chutes and contact systems sized for high fault currents. Modern air circuit breakers use electronic trip units that allow precise settings and support advanced functions, such as: Fine-tuned long-time, short-time, instantaneous, and ground fault elements Communication and logic features that enable zone-selective interlocking and remote High Voltage Breaker Technologies at the Grid InterfaceHigh-voltage breakers sit at the interface between the power plant and the grid, or between medium-voltage systems and high-voltage transmission. Two key technologies dominate: Vacuum circuit breakers for medium voltage up to about 40.5 kV SF6 gas breakers for high voltages from roughly 72 kV up to 800 kVThese high-voltage breakers must interrupt very large fault currents quickly enough to protect generator step-up transformers and prevent severe grid disturbances. Overload Protection Breaker vs Short Circuit ProtectionAn overload protection breaker responds to currents that are above normal but not instantly destructive. The thermal element in a molded case breaker or miniature breaker trips when conductors or windings would otherwise overheat and fail. Short-circuit protection operates at much higher current levels and trips almost immediately through the magnetic element, preventing conductors, busbars, and equipment from experiencing catastrophic mechanical and thermal forces. Both functions must be present and correctly set for cables, motors, and transformers in high-duty industrial environments. Summary Table: Matching Breaker Types to Typical Duties This mapping helps a plant engineer or designer quickly align breaker type to duty.Breaker type Typical voltage level Typical duty in power generation / heavy industry Mini circuit breaker Low-voltage branch circuits Control panels, instrumentation, small auxiliary loads, and local lighting Molded case breaker Low-voltage feeders and large loads MCC feeders, large pumps and fans, distribution panels, and localized breaker panel sections Air circuit breaker Main low-voltage switchgear Main incomer, generator LV connection, bus couplers, tie breakers in plant LV switchgear High-voltage breaker Medium and high voltage levels Generator circuit breaker, grid connection, step-up transformer protection, MV distribution to large loads When engineers shortlist industrial circuit breakers for a power plant or heavy industrial project, they need reliable, specification-grade devices in each category. To centralize sourcing and standardize breaker selections across an industrial fleet, visit the circuit breakers section on eINDUSTRIFY. Our selection provides molded case breakers, mini circuit breakers, main breaker kits, and related hardware from verified manufacturers, ready to serve your industrial needs. How Industrial Breakers Keep Plants Safe and OnlineWhen a fault occurs, sensors in the industrial circuit breakers detect the overcurrent and initiate a trip in accordance with the time-current characteristics set for that system level. If breaker types and settings are properly matched to the system, the fault is cleared quickly at the correct level, and the rest of the plant continues operating. Protecting People from Arc Flash and ShockArc flash incidents occur an estimated 5 to 10 times per day in the United States, with around 30,000 incidents, 7,000 burn injuries, and roughly 400 deaths each year. Most arc flash fatalities happen because of burns, not direct shock, and many events occur around circuit breaker connections in panels and switchgear. Industrial circuit breakers and breaker panels influence arc flash risk through: Clearing time: Faster fault clearing reduces incident energy at the point of fault Coordination: Preventing upstream industrial breakers from tripping late and exposing workers to higher energy levels Panel design: Arc-resistant breaker panels, remote operation, and proper maintenance of industrial breakers lower the risk of severe eventsProtecting Generators, Transformers, and CablesA generator circuit breaker that fails to open correctly can leave a generator motoring, with severe unbalanced currents and mechanical stress on the shaft. High-voltage breakers at the generator and grid interface must interrupt faults quickly enough to keep step-up transformers within thermal and mechanical limits. On the low-voltage side, correctly chosen molded case breakers and air circuit breakers limit let-through energy to protect: Generator stator connections and bus ducts Auxiliary transformers feeding plant loads Cables to critical motors and process equipment Protecting Uptime and Avoiding Nuisance TripsFalse tripping accounts for 42 percent of circuit breaker failures in distribution systems, often tied to miscoordination or relay issues. Each nuisance trip on an industrial breaker can force process shutdowns, thermal cycling, and costly restart sequences in turbines, boilers, or large mills. Correctly sized and set overload protection breakers on feeders and motors helps: Ride through typical inrush and short overloads. Trip only when an overload would damage cables or equipmentCoordination and Advanced Protection Features in Industrial Circuit BreakersCoordination is the difference between losing one feeder and losing a whole bus or generator. In coordinated schemes, industrial circuit breakers at each level trip in a predictable order, based on their time-current curves and logic. Selective Coordination: Containing FaultsSelective coordination ensures that the breaker closes to the fault of trips first, while upstream industrial breakers remain closed. In a miscoordination case, a data center experienced a wider outage when the upstream breaker operated instead of the local breaker at the faulted branch. In a power plant, selective coordination between mini circuit breakers, molded case breakers, and the main air circuit breaker prevents a fault on a single motor from tripping the main switchgear or generator breaker. Zone Selective Interlocking (ZSI) in Modern BreakersZone-selective interlocking uses communication between electronic trip units so that industrial breakers can “tell” upstream devices when a fault is detected. If a downstream breaker detects a fault and sends a restraint signal, the upstream breaker waits; if it sees fault current without a restraint signal, it trips quickly because the fault is in its zone. ZSI lowers fault-clearing times where they matter and reduces the incident energy of faults within breaker panels and switchgear. It also maintains coordination while still providing fast clearing in zones where no downstream breaker is present to clear the fault. Trip Curves and Settings Without the MathIndustrial electronic trip units allow you to shape breaker response using: Long-time elements that define overload behavior Short-time elements that manage high but brief currents Instantaneous elements that trip very quickly on severe faults Ground fault elements that detect and clear earth faultsIn practical terms, this means an engineer can tune a molded case breaker or air circuit breaker: High enough to ride through motor and transformer inrush Low and fast enough to clear real faults without sacrificing cables, busbars, or connected equipmentDesigning selective coordination and ZSI schemes is only effective if the actual industrial breakers installed match the required capabilities. On eINDUSTRIFY's circuit breaker category, engineers can link protection design decisions with practical, repeatable sourcing, enabling them to shortlist molded case breakers, mini circuit breakers, main LV breakers, and associated components that support the protection strategy they have defined. What Goes Wrong When Industrial Breakers Are Misapplied Failure data show several recurring patterns in industrial and utility settings. They are highly relevant to power generation and heavy industry operations. Typical Failure Modes in Circuit BreakersAn extensive study of distribution system equipment reports the following failure mode distribution for circuit breakers: Failure mode Share of failures Opened when it should not (false tripping) 42% Failed while in service (not opening or closing) 32% Failed while opening 9% Damaged while successfully opening 7% Failed to close when it should 5% Damaged while closing 2% Failed during testing or maintenance 1% Damage found during testing or maintenance 1% Other 1% False tripping directly affects uptime, while failures to open or close on command create serious safety and asset risks. Root Causes from Heavy Industry and Oil and GasThe Norwegian Petroleum Safety Authority analyzed multiple breaker incidents at offshore and onshore facilities and found recurring issues: Aging equipment with no clear service life criteria or replacement planning Technical design weaknesses and misdimensioning, where the wrong industrial breakers were specified for duty Frequent start/stop operation of large drives without an appropriate breaker choice Missing barriers and inadequate arc flash mitigation Maintenance weaknesses that failed to detect developing breaker problemsIn one generator breaker failure case, two poles continued conducting after a trip command, motoring the machine with severe unbalanced currents. In several industrial blackout investigations, misconfigured or failed high-voltage breakers contributed to total plant blackouts and long restart times. Trends Shaping Industrial Circuit Breakers in 2024–2026Industrial circuit breaker technology is evolving with digitalization, environmental pressures, and changing generation portfolios. Smart and Digital Industrial BreakersModern molded case breakers and air circuit breakers increasingly include: Embedded metering and communication for real-time monitoring Event logging and diagnostics that support predictive maintenance Integration into plant SCADA and asset management systems That helps operators detect degrading industrial breakers before they fail in service and supports data-driven decisions about maintenance and replacement. SF6-Free and Vacuum-Based High Voltage BreakersThe industry is seeking alternatives to SF6 because of its high global warming potential. Vacuum technology is expanding into higher voltage ranges, and SF6-free switchgear options are appearing in more applications. These high-voltage breaker developments matter for generator and grid interfaces, especially in new plants and retrofit projects that must meet tighter environmental targets. Renewables, Microgrids, and Complex Operating ModesMore renewables and microgrids introduce bidirectional power flows, more frequent switching, and new fault profiles. That increases the importance of industrial circuit breakers with flexible protection settings and robust mechanical endurance. In power generation, these trends show up as: More complex coordination between generator breakers, feeder breakers, and intertie breakers. Higher expectations for breaker data and remote configuration capabilities. Turning Breaker Choices into Safety and UptimeA single downstream fault does not have to cause a plant to go dark. The difference lies in whether the industrial circuit breakers and breaker panels were correctly selected, coordinated, and maintained across the system's low-, medium-, and high-voltage levels. For power generation and heavy industrial facilities, getting industrial breakers right means: Lower arc flash risk and better personnel safety Better protection for generators, transformers, and cables Fewer nuisance trips and faster recovery from real faultsEngineers and maintenance teams specifying molded case breakers, air circuit breakers, mini circuit breakers, high voltage breakers, or complete breaker panel assemblies need reliable sourcing. eINDUSTRIFY lets compare and procure industrial circuit breakers, matching fault levels, coordination plans, and safety requirements across power generation and heavy industry use cases.
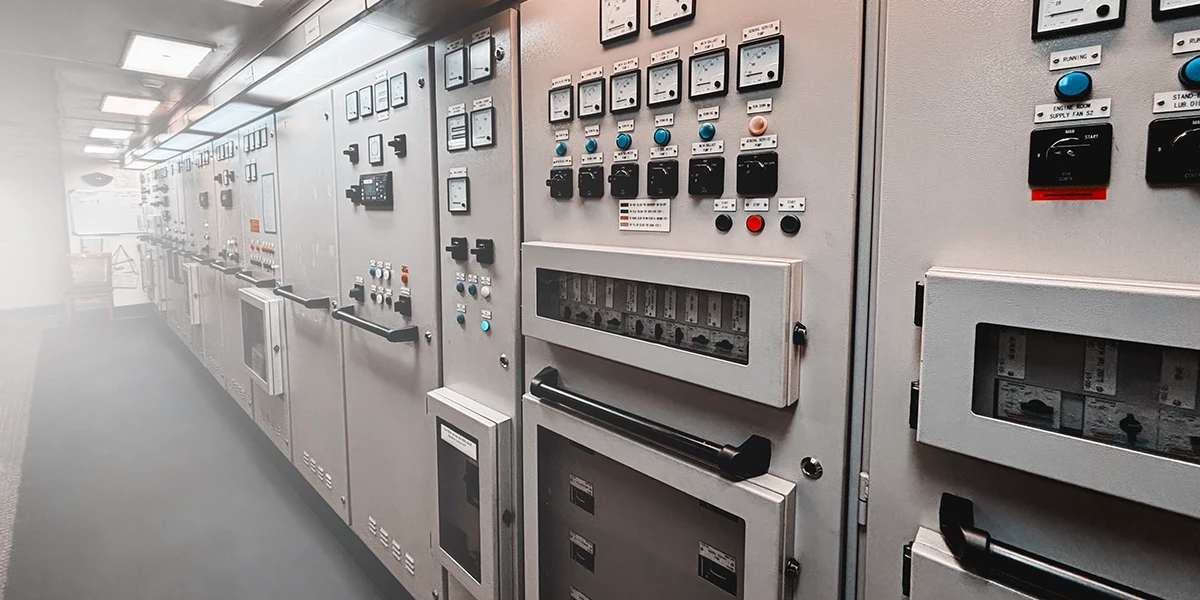

In most power generation facilities, the single-line diagram looks neat and controlled. In reality, the low-voltage side often tells a story of additions over the years, different generations of boards, and a mix of ratings and layouts that were never designed as one system. The result is an electrical backbone that technically works but makes fault coordination, maintenance, and expansion harder than they need to be. As plants add generators, renewables, and more auxiliaries, power distribution panels, ranging from the main distribution panel and switchboard panel down to feeder panels, industrial panels, and local distribution boards, have become the real anchor of reliability and optimization. When these panels are specified and organized coherently, they turn a complex network into one that is easier to protect, monitor, and expand. When they are treated as commodity boxes, they quietly cap uptime and flexibility. For readers who are ready to compare actual hardware options as they plan, you can explore standardized power distribution panels (main, feeder, and distribution boards) in the eIndustrify Distribution Panels Catalog. This guide walks plant and electrical engineers through how to use power distribution panels to deliberately shape an industrial or power-gen setup, improving selectivity, safety, and future capacity while staying aligned with modern low-voltage standards and realistic operating conditions. Structuring Power Distribution Panels in Power-Gen Facilities From Single Line to Panel Architecture On a single-line diagram, a typical power-generation facility shows the generator and utility sources feeding a transformer, then an LV bus, and then loads. In practice, that LV bus is implemented as a main distribution panel (LV switchboard) that then feeds multiple feeder panels and local distribution boards across the plant. A practical architecture in a power-gen site looks like this: gen site looks like this: Generator step-down transformer and/or utility incomer → Main distribution panel / LV switchboard panel in the switchgear room → Feeder panels / industrial panels serving plant areas: turbine hall, boiler island, common services, water treatment, balance-of-plant →of plant → Local distribution boards near loads (MCC rooms, control buildings, lighting boards, admin zones). All of these are power distribution panels, just at different levels of the hierarchy. Optimizing your industrial setup means deliberately coordinating this hierarchy, rather than letting it evolve into a collection of unrelated boards. What Are You Optimizing For? In a power-gen facility, good distribution design balances three priorities: gen facility, good distribution design balances three priorities: Uptime and selectivity (faults stay local and don’t trip upstream panels). Safety and maintainability (panels support safe operation and maintenance, with appropriate internal separation and clear access). Future flexibility (the system can accept more generators, more auxiliaries, or digital monitoring without needing to be rebuilt). Low-voltage distribution systems are now expected to support energy efficiency, power quality, and system reliability, not just carry current. If the main distribution panel is undersized, if feeder panels are scattered without a clear zoning concept, or if distribution boards are loaded arbitrarily, those three priorities start conflict rather than reinforce each other. Main Distribution Panel – The Plant’s Electrical Anchor Role Of the Main Distribution Panel in A Power-Gen Facility The main distribution panel, often implemented as an LV switchboard panel, is the electrical anchor of the facility. It receives power from the generator step-down transformer and/or utility incomer and then feeds: Major feeders to turbines, boilers, and balance-of-plant MCCs. of plant MCCs. Sub-distribution feeder panels serving large plant zones distribution Sometimes, direct large motor loads and essential services. Modern LV switchboards are increasingly described as the “nerve center” of industrial power distribution, because they centralize control, protection, and monitoring of multiple sources and loads. For a power-gen plant, this is where you decide how much fault energy the system can tolerate, how loads are structured, and how easily you can isolate, expand, or reconfiguring plant, this is where you decide how much fault energy the system can tolerate, how loads are structured, and how easily you can isolate, expand, or reconfigure. Key Design and Rating Decisions When you specify or review a main distribution panel, a few design decisions have outsized impact: System voltage and configuration – confirm the panel is designed and tested for your nominal voltage (e.g., 400 V, 480 V, 690 V) and system grounding (solidly grounded, impedance-grounded, etc.). grounded, etc.). Continuous current rating with realistic margin – size the incomer and busbars not just for today’s load but for plausible future additions, like an extra auxiliary system or another generator on the same bus. Short-circuit withstand rating – verify the panel’s short-circuit rating (kA for a specified duration) exceeds the calculated prospective fault level at its location; industrial LV power distribution panels are explicitly rated for fault withstand under IEC frameworks. circuit withstand rating (kA for a specified duration) exceeds the calculated prospective fault level at its location; industrial LV Form of separation and enclosure – higher forms of internal separation and appropriate ingress protection (IP) ratings improve safety and enable selective maintenance without exposing live parts, which is critical in power-generating environments. Compliance with IEC 61439 – IEC 61439 defines how low-voltage switchgear assemblies should be designed, verified, and coordinated, including device selection, wiring, and suitability for real operating conditions. Many industrial projects now also adopt supplementary requirements that demand features such as shunt trips for remote tripping, clear external position indication, and front-operable breakers to improve operability and safety. Practical Optimization Moves on the Main Board Practical ways to use the main distribution panel to optimize your setup: Standardize on a capable switchboard platform – choose a switchboard panel design that can accept advanced metering, communication modules, and additional feeders later, even if you don’t populate them immediately. Use electronic trip units on main breakers – with adjustable long-time, short-time, and instantaneous settings- to coordinate with downstream feeders and capture load data for future optimization. Reserve physical and thermal space – specify busbars and enclosures with documented spare capacity for additional feeder breakers or tie breakers, so future expansion doesn’t require a complete replacement. Feeder Panels and Industrial Panels – Localizing Risk and Complexity What Feeder Panels Actually Do in A Plant Once power leaves the main distribution panel, it typically flows into feeder panels or industrial panels that serve specific zones or systems: Turbine hall auxiliaries. Boiler and flue-gas systems Cool water and balance-of-plant. Common services (HVAC, lighting, workshops). These power distribution panels take the high-level capacity of the main board and break it into manageable chunks. Their job is to keep faults and maintenance localized to a zone, so that a problem in one area does not compromise the whole plant. level capacity of the main board and break it into manageable chunks. Their job is to keep faults and maintenance localized to a zone, so that a problem in one area does not compromise the whole plant. Industrial distribution panel guidance stresses that sub-distribution boards should be engineered with appropriate short-circuit ratings and device selection for their position in the system, not treated as generic boxes. Feeder Panel Design Considerations When specifying or upgrading feeder panels/industrial panels, several parameters drive real-world behavior: Short-circuit rating at their location – the prospective fault current at a feeder panel may be lower than at the main board, but still high enough to demand serious fault withstand performance from the panel and its breakers. Circuit rating at their location Number of outgoing ways and spares – under-sizing the number of feeders encourages “temporary” extensions and overcrowded panels; well-designed industrial panels allow room for additional circuits and clear cable management. Environmental robustness – panels in hot, dusty, corrosive, or outdoor locations need appropriate enclosure ratings and mechanical design to maintain reliability. Logical grouping of feeders – grouping outgoing feeders by system (e.g., all boiler auxiliaries in one industrial panel) maps your electrical layout to the plant’s process layout, simplifying operations and faultfinding. Selectivity And Coordination Between Main and Feeder Panels From a protection standpoint, the main distribution panel and feeder panels must be coordinated so that: For a fault within a feeder panel, its outgoing or incomer breaker trips first. The main incomer only trips for failures in the panel’s own bus or for backup of extreme faults. Engineering checklists emphasize plotting time–current curves for upstream and downstream devices and choosing breakers and settings that preserve selectivity, especially in industrial LV systems. Poorly matched electrical panel components, for example, a fast-acting main breaker feeding slower downstream MCCBs, can make the main panel “see” every local fault and trip first. A simple optimization is to standardize a family of molded-case or air circuit breakers with compatible trip units across the main and feeder levels, ensuring predictable coordination and support from manufacturer data. case or air circuit breakers with compatible trip units across the main and feeder levels, so coordination is predictable and supported by manufacturer data. Distribution Boards – Optimizing Auxiliary and Control Circuits Role Of Local Distribution Boards At the edge of the hierarchy are distribution boards that supply final auxiliary and control circuits, such as: Local control power for MCCs and process skids. Control rooms, PLC, and DCS cabinets. Critical small‑power and lighting for operational areas within the station. In a power‑generation context, distribution boards are the final step in delivering power from the main switchboard panel into the control and balance‑of‑plant systems that keep units online. Although they carry smaller currents than main and feeder panels, how you design and operate these boards strongly influences: Nuisance tripping interrupts critical auxiliaries. How quickly can engineers identify, isolate, and restore faulty circuits? The safety and predictability of routine isolation and maintenance of live plants. Layout And Component Choices That Matter When you are optimizing a distribution board for an industrial or power‑gen site, layout is a design decision, not just a wiring detail: Logical circuit grouping by system – group ways by process or equipment package (e.g., all condensate‑system auxiliaries together) so that protection, isolation, and future expansion are easier to plan at an engineering level. Specification of breakers and RCDs – select breaker characteristics and any residual‑current protection based on load type, fault levels, and coordination with upstream power distribution panels, rather than using a one‑size‑fits‑all device lists. Built‑in isolation capability – ensure the board design includes clear incoming and section isolation points that support your plant’s lockout‑tagout and maintenance strategy without taking down unrelated systems. Framing these as part of the specification for a distribution board, rather than ad‑hoc decisions in the field, keeps the final level of your power distribution panels hierarchy aligned with the same engineering and procurement logic as your main and feeder panels. Electrical Panel Components That Drive Performance Inside every power distribution panel are electrical panel components whose selection directly impacts uptime, safety, and efficiency. Incoming And Outgoing Breakers Incoming ACBs and MCCBs, and outgoing feeder breakers, are the primary protective devices in each panel: Their interrupting capacity must exceed the prospective fault level at their location. Electronic trip units with adjustable settings support selective coordination, load recording, and remote monitoring. Choosing breakers from compatible families across your main distribution panel, feeder panels, and distribution boards makes it easier to build clean, verifiable coordination schemes. Busbars And Busbar Systems Busbars carry the actual current through the panel: Cross-section and material must be sized for both continuous current and short-circuit thermal and mechanical stresses. Proper supports, clearances, and segregation reduce the risk of internal faults and support higher forms of separation under IEC 61439. Under-sized or poorly supported busbars limit your ability to add feeders or uprate loads later without major rework. Metering And Communication Modules Modern LV switchboard panels and industrial panels increasingly incorporate: Multi-function meters on incomers and key feeders. Communication gateways (Modbus, Ethernet) linking the panel into plant SCADA or energy management systems. Integrating metering and communications enables operators to optimize load distribution, identify inefficiencies, and troubleshoot more quickly. Energy-efficiency guidance for industrial LV systems stresses the value of regular monitoring and analysis to improve power distribution. efficiency guidance for industrial LV systems Surge And Power Quality Devices Integrating power-quality components directly into power distribution panels helps protect sensitive plant equipment: quality components directly into Surge protective devices (SPDs) at main and feeder panels clamp transient overvoltage caused by switching, faults, or lightning events. Harmonic filters and power factor correction banks, when appropriate, improve overall efficiency and power quality in industrial facilities. Mechanical And Safety Features The mechanical design of panels also matters: Interlocks, clear position indication, and robust door and hinge systems make operation safer and reduce the chance of human error. Compartmentalization and front access can allow many routine tasks to be done without exposing live parts, which is a key expectation in modern LV switchboard panel standards. The takeaway is that optimizing your industrial setup is as much about how you specify and integrate electrical panel components as it is about the panel enclosure itself. Turning Panels into an Optimization Strategy (Not Just Hardware) From Patchwork Boards to a Coherent Platform Many power generation sites have grown over the decades. Every new project or retrofit added to another industrial panel, another distribution board, and another small switchboard panel. Over time, this creates a patchwork of different ratings, manufacturers, and philosophies. Industry analysis of power distribution panels indicates that global demand is shifting toward more standardized, modular, and smart panel platforms for industrial applications, as they are easier to engineer, operate, and expand. Moving toward a coherent set of power distribution panels, standard main distribution panels, feeder panels, and distribution boards built on consistent design rules, lets you: Apply one clear coordination philosophy across the plant. Simplify spares and training. Implement monitoring and optimization in a repeatable way across units or sites. Practical steps for engineers and buyers When you are planning a new project or a major upgrade, a simple workflow is: Map your current hierarchy: identify every main distribution panel, feeder panel, and distribution board in the system. Check ratings and fault levels at each panel and compare them with the calculated short-circuit duties. Flag panels that are under-rated, impossible to maintain safely, or known coordination “trouble spots”. For replacement or new panels, build a short specification based on: IEC 61439 compliance, adequate short-circuit and thermal ratings, clear internal separation, compatible breaker families, and provision for metering/communications. When you reach the sourcing step, platforms like eIndustrify give you a centralized way to compare and source power distribution panels, from main distribution panels and feeder panels to smaller distribution boards, that match these criteria and can be standardized across your industrial or power-generation fleet. generation fleet.
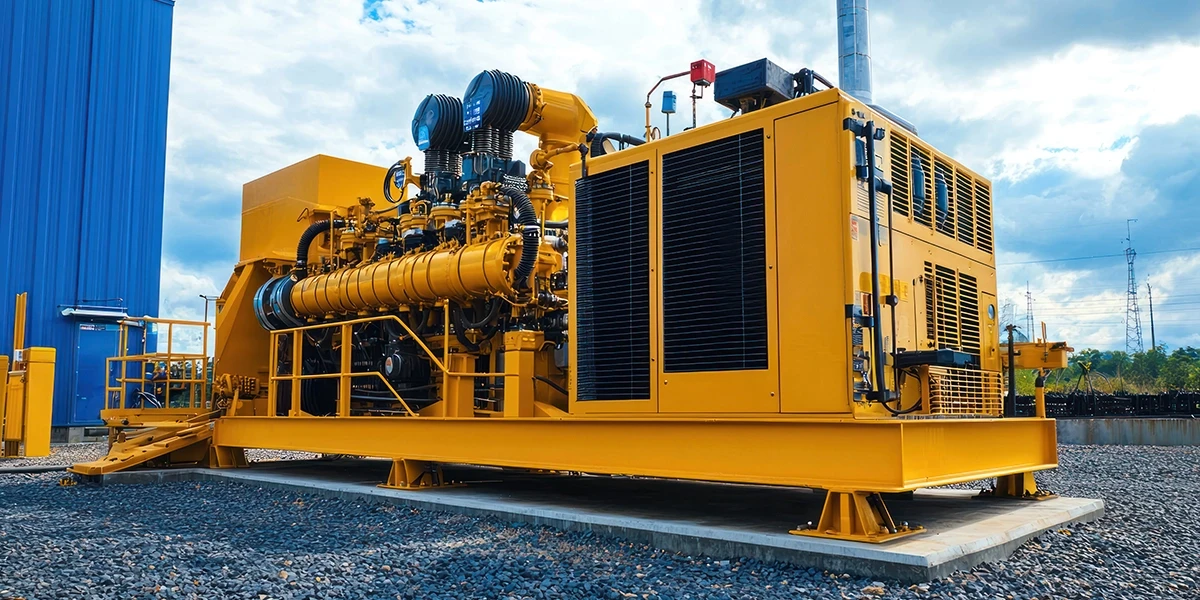

Picture a single-phase to ground fault on a downstream motor feeder that trips the generator breaker, shuts down an entire plant, and turns what should have been a localized outage into a full-site incident report. In post-incident reviews, the root causes are usually misapplied or poorly coordinated generator protection devices that cannot distinguish between a local feeder fault and a system-level problem. Today's generators power everything from hospital life-safety systems to high-density racks in data centers and renewable-heavy microgrids, often within the same campus or facility. Yet many of these critical systems still rely on a patchwork of legacy breakers, transfer switches, and relays that were never designed to work together or to meet current coordination expectations from NFPA 110 and the NEC. The result is a widening gap between the complexity of the power system and the fundamental nature of its protection layer. This guide walks site engineers through five essentials generator protection devices: Generator breaker Automatic transfer switch Surge protector Ground fault device Voltage sensor and phase monitor For each device, we will connect its role to fundamental failure modes, such as nuisance trips during motor starts, undetected ground faults, and slow-burning phase unbalance damage. Protection Philosophy 101: Before You Pick Devices Good generator protection devices are selected and set based on a clear understanding of these priorities and operating scenarios.: At the machine level, protection functions keep stator windings, rotor circuits, insulation systems, and excitation hardware within safe thermal and dielectric limits during abnormal conditions. At the system level, generator protection must prevent faults on one feeder or bus from propagating and cascading into an entire emergency power system or microgrid. On the human side, protective devices help limit shock and arc-flash energy by clearing faults quickly and in a controlled, selective manner that aligns with NEC and NFPA expectations. flash energy by clearing faults rapidly and in a controlled, selective way that aligns with NEC and NFPA expectations. These objectives overlap in practice. A ground fault left undetected might not immediately destroy the generator, but it can elevate touch voltages and arc flash risk throughout the system. An oversensitive generator breaker that trips on every downstream disturbance might technically protect the machine. Still, it compromises uptime and defeats the purpose of having standby or prime power available. flash risk throughout the system. An oversensitive generator breaker that trips on every downstream disturbance might technically protect the machine. Adequate generator protection, therefore, starts with a clear view of what you are trying to protect, in what order of priority (people, generator, loads, upstream grid), and under which operating scenarios. Generator Breaker: Your First and Last Line of DefenseWhat a generator breaker does A generator breaker (generator circuit breaker, or GCB) is the central switching and protective interface between the generator and the rest of the system, connecting or isolating the machine from the main bus or step-up transformer while interrupting any fault current the generator can supply. It typically sits at the generator terminals or on the low-voltage side of the step-up transformer, and it must combine an adequate continuous current rating, fault-interrupting strength, mechanical endurance, and a clean interface to the protection relay that sends it trip commands. Sizing and rating beyond "amps on the nameplate." Properly sizing a generator breaker means checking both its thermal rating for expected load (with some growth margin) and it short-circuit rating against the maximum generator-source and system-source fault currents at its location, not just matching full-load amps. Because generators have high X/R ratios that create asymmetrical fault currents with high peak values, you also need to confirm the breaker's tested asymmetry capability and ensure its interrupting and making ratings are compatible with the relay's intended clearing times. Coordination with downstream protection Coordination issues, not under sizing, cause many of the most disruptive generator trips, especially when a downstream fault in a transfer switchboard trips the generator breaker instead of the feeder or branch breaker. To prevent this, the generator breaker's time-current characteristic must be plotted against the downstream breakers so that the downstream devices operate first across the expected fault range. At the same time, the settings also account for motor inrush and transformer energization, so that normal starting currents do not appear as faults. Checklist for specifying a generator breaker When selecting or reviewing a generator breaker, a simple checklist can help reduce the risk of missing a critical detail. Key items include: Voltage class and insulation level that match the generator terminals or the secondary voltage of the step-up transformer. Continuous current rating with margin for realistic load growth and potential future paralleling or export operation. Interrupting and verifying capacities against calculated generator source and system source fault duties at the breaker location. Source and system source fault duties at the breaker location. Short time withstand rating adequate for the longest plausible fault clearing times from upstream or downstream protection. Clearing times from upstream or downstream protection. Selective coordination with downstream automatic transfer switches and distribution breakers, confirmed by plotted curves rather than assumptions. Mechanical endurance consistent with expected numbers of operations in testing, paralleling, and load-shedding sequences. Interface compatibility with the chosen generator protection relay, including trip coil voltage, auxiliary contacts, and any required communications. Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Getting Power to the Right Loads at the Right Time Why ATS selection is a protection decision An automatic transfer switch is more than a big contactor; it continuously monitors the preferred source, decides when to bring the generator online, and controls how and when loads move between sources. Its logic directly affects which loads experience a momentary outage, which transfers occur without interruption, and how well the generator breaker and downstream protection remain coordinated during source changes. Core ATS types and when to use them Open transition ATS units use a break-before-make sequence, briefly disconnecting the load from one source before connecting it to the other, which is acceptable when short interruptions do not harm equipment. Closed transition ATS units use a make-before-break sequence, momentarily paralleling the two live sources to provide essentially seamless transfers for sensitive loads in data centers, hospitals, and other mission-critical facilities. Open-delayed transition adds an intentional pause between sources, so residual voltages and transients can decay, which can help when large motor or transformer loads are involved. Transition ATS units use a make-delayed transition, which adds an intentional pause between sources to allow residual voltages and transients to decay, which can help when large motor or transformer loads are involved. Key specs engineers often miss Beyond ampere rating, three ATS attributes strongly influence generator protection performance: source-sensing thresholds, transfer timing, and withstand/closing ratings. Voltage and frequency pickup and dropout settings determine when the ATS decides a source is "bad" or "good," transfer and retransfer delays shape how often the generator starts and how long it carries load, and the ATS's withstand and closing ratings must match available fault currents so it can safely make and break under emergency conditions. Mini use cases In hospitals, NFPA 110 and NFPA 99 drive separate life-safety, critical, and equipment branches, so ATS selection and settings determine which circuits restore within 10 seconds and how coordination is maintained at each switch. In data centers, closed-transition ATS schemes are often paired with UPS systems, so the ATS must transfer without causing voltage steps or sags that force the UPS fleet to go to battery unnecessarily. Surge Protector: Shielding Against Transient Overvoltage Why generators are hard on sensitive loads Generator systems experience frequent switching events, steep load steps, and occasional utility disturbances or nearby lightning, all of which can cause transient overvoltage's that stress insulation and damage sensitive electronics. Without a dedicated surge protector device, these fast spikes ride on top of the generators output and can silently shorten the life of transfer switch controls, building automation systems, and IT hardware. SPD basics for generator systems Surge protective devices are grouped into Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3, based primarily on where they are installed and the types of surges they protect against. Type 1 SPDs are installed at the service entrance or main switchboard to handle large external surges; Type 2 SPDs are installed in distribution panels or generator switchboards to clamp residual and internally generated surges; and Type 3 SPDs are installed close to sensitive loads to capture the last, lower-energy transients at the point of use. Designing a layered surge protection strategy An effective generator surge strategy usually combines all three SPD types, so no single device is asked to absorb every surge. A typical pattern is to install Type 1 protection at the service or main emergency switchboard, Type 2 devices on generator and critical distribution panels, and Type 3 protection at key endpoints such as IT racks, control panels, and medical imaging loads that are particularly sensitive to voltage spikes. Common mistakes Two frequent mistakes are installing a single SPD and assuming that the whole facility is protected, and overlooking grounding and bonding quality, which is essential for any SPD to work correctly. Another is selecting SPDs solely on surge current rating while ignoring residual (let-through) voltage, which appears at the terminals of sensitive equipment during a surge event. Ground Fault Devices: Catching the Faults You Cannot See Ground fault protection vs overcurrent protection Many dangerous ground faults do not produce enough current to quickly trip standard overcurrent devices, especially if the fault path is resistive or involves long cable runs. A ground fault device does what standard overcurrent relays often cannot: detect low-level ground faults that do not produce enough current to trip a breaker quickly. How ground fault protection works in generator systems In generator applications, ground-fault protection is often provided by zero-sequence current sensors or residual-current relays that compare the vector sum of the three-phase currents (and sometimes the neutral) to a pickup threshold. More advanced schemes, such as restricted earth-fault protection on wye-connected machines, use separate current transformers on each phase and the neutral to distinguish internal stator ground faults from external faults, so the relay trips only when the generator itself is at risk. Code-driven decisions for emergency systems NEC and NFPA requirements complicate ground-fault decisions for emergency and legally required standby systems, because unwanted trips of the source can be more dangerous than a controlled alarm. For example, NFPA 110 requires coordination of overcurrent devices with each ATS for emergency power supply systems. Many designers implement a ground-fault alarm only on emergency generators, using a ground-fault trip on downstream distribution, so a ground fault can be located and cleared without dropping the entire source. Practical configuration tips Practical settings aim for a pickup level high enough to ride through transformer inrush and normal leakage, but low enough to detect genuine ground faults in a reasonable time. Equally important is documenting and verifying the neutral-to-ground bonding point for the generator or generator bus, because misplaced or duplicate bonds can bypass ground-fault elements or cause circulating currents that lead to misleading measurements and nuisance alarms. Voltage Sensor and Phase Monitor: Preventing Slow Burn Failures Why is voltage and phase monitoring non-negotiable now Overvoltage, under voltage, phase loss, and phase unbalance can quietly damage equipment, which is why a dedicated voltage sensor and phase monitor are no longer optional. Voltage and phase monitoring relays give you early warning and, when wired to trip or alarm, can disconnect vulnerable loads before a slow-burning issue becomes a major failure. What a phase/voltage monitoring relay watch A typical voltage sensor or three-phase monitoring relay tracks line-to-line or line-to-neutral voltage, checks that each phase remains within an over- or under-voltage band and verifies that all three phases are present in the correct sequence. It can also measure phase-to-phase imbalance and, if the deviation exceeds a set percentage for longer than a defined delay, raise an alarm or open a control contact to protect connected equipment. Applications across standby, prime, and microgrids In standby and rental sets feeding mixed motor loads, voltage and phase monitors help ensure that a loose connection, a failed fuse, or a contactor problem does not leave a motor running on two phases. In microgrids and hybrid systems with renewables, these relays provide a simple way to monitor voltage quality and phase balance as sources come online or offline, supporting more sophisticated controls without relying entirely on them. Configuration pointers In practice, many engineers set the phase of unbalance pickup to 5–10 percent, with a short time delay to ride through brief disturbances without ignoring persistent problems. Placing monitoring relays at key distribution points, such as the generator output, main emergency switchboard, or large motor control centers, provides operations teams with actionable information about where a voltage or phase issue is developing, rather than just a downstream symptom. Turning Devices into a Protection Strategy Choosing the right generator protection devices is only half the job; making them work together as a layered, coordinated system is what actually prevents minor faults from escalating into full-site outages. By treating the generator breaker, ATS, surge protection, ground fault devices, and voltage and phase monitors as complementary tools rather than standalone components, onsite engineers can align machine safety, system reliability, and code requirements in a single, coherent protection scheme that is much easier to operate, troubleshoot, and upgrade over time. And when it is time to specify or replace hardware, platforms like eINDUSTRIFY give you a single place to compare, select, and source the protection devices that fit your design criteria.
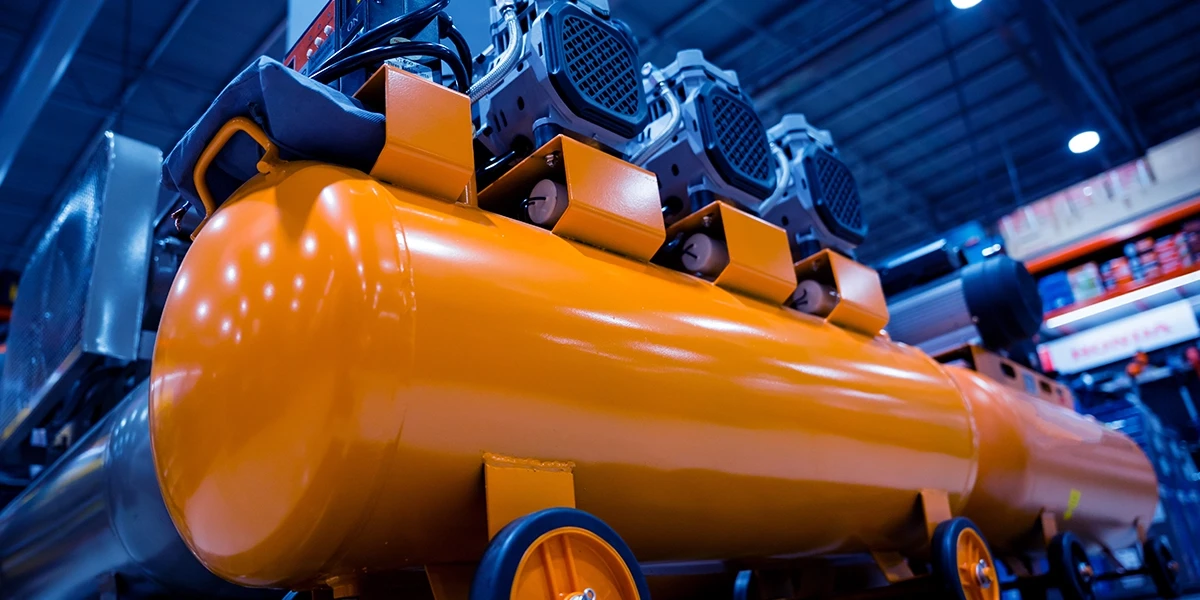

In modern manufacturing and industrial operations, compressed air is vital for powering equipment, tools, and processes. It drives everything from pneumatic tools and automated machinery to material handling systems and packaging lines. Choosing the right industrial air compressors is important for any facility. It affects performance, energy efficiency, and long-term costs. This guide helps you learn the basics of air compressors. It covers their types, uses, and how to choose the best one for your facility.Introduction to Industrial Air Compressors These compressors convert power, usually from an electric motor, diesel engine, or gasoline engine, into compressed air. This pressurized air powers machinery, actuates valves, drives tools, and supports industrial air applications such as painting, sandblasting, and pneumatic conveying. Air compressors are designed to run continuously, while residential ones are not. They support plant air systems where reliability, pressure stability, and energy efficiency are essential.How Does Compressed Air Work? Compressed air works by reducing the volume of air and increasing its pressure, then storing it for later use. The compressor takes in air and compresses it using different mechanisms, depending on the type of compressor. Pressurized air flows through the air system, where filters, dryers, and regulators condition it before use. Compressed air energy, stored power, is widely used in industries for assembly lines and robotics.Main Types of these Compressors: Rotary Screw Air Compressors: Compressor Type: Rotary Screw Air CompressorsDescription: Use two helical rotors to compress air efficiently and deliver a steady flow rate (CFM) and pressure (PSI). Ideal for continuous operation.Best For: Manufacturing plants, automotive industries, and continuous production lines.Benefits: Low noise, consistent airflow, high efficiency.Drawbacks / Tips: Tip: Consider Variable Speed Drive (VSD) compressors for improved energy efficiency. Reciprocating (Piston) Air Compressors Compressor Type: Reciprocating (Piston) Air Compressors Description: Use pistons to compress air within cylinders. Suitable for smaller operations that require intermittent air supply.Best For: Workshops, smaller facilities, and short-duration tasks.Benefits: Simple design, low upfront cost, easy maintenance.Drawbacks / Tips: Drawback: Higher noise levels and limited duty cycle. Centrifugal Air Compressors Compressor Type: Centrifugal Air Compressors Description: Use impellers to accelerate and pressurize air. Ideal for high-demand environments requiring large volumes of compressed air at constant pressure.Best For: Refineries, chemical plants, large-scale production facilities.Benefits: Oil-free operation, minimal vibration, continuous outputDrawbacks / Tips: Drawback: Higher initial investment and complex maintenance. Rotary Screw vs. Reciprocating Compressor When comparing rotary screw vs. reciprocating compressors, consider your application's runtime and load. Rotary screw compressors outperform reciprocating types in reliability, energy efficiency, and noise control. However, reciprocating compressors are cost-effective for smaller setups with limited air usage. Large factories often rely on rotary screw compressors for their steady airflow and long-lasting operation.Industrial Air Applications Compressed air powers a wide range of industrial applications, including: Manufacturing lines: operating tools, machinery, and actuatorsPharmaceuticals: clean, oil-free air for production processes Automotive: painting, assembly, and tire inflationEnergy sector: instrumentation and control systems Understanding industrial air usage helps you correctly size and configure your compressed air system.Air System Components A well-designed industrial compressed air system includes more than just the compressor. It consists of several essential air system components that ensure a clean, dry, and stable air supply: Air Dryer: It removes moisture, preventing corrosion and contamination. Eliminating water vapor from the air stream ensures the longevity and reliability of pneumatic tools and equipment.Air Filters: It traps dust, oil, and particulates. These filters protect downstream components from damage and maintain optimal airflow quality throughout the system.Air Receiver Tank: It stores compressed air and balances system pressure. It acts as a buffer to handle demand fluctuations and reduce compressor cycling, improving overall system efficiency. Regulators and Valves: It controls air pressure and flow. They ensure consistent performance and safety by maintaining the correct pressure levels for various operationsAir Treatment Equipment: It enhances air quality for sensitive applications. This equipment is vital for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where clean, dry air is essential. Each component plays a key role in maintaining the efficiency of the industrial air system.Air Pressure Requirements for Industrial Use Selecting an air compressor depends on your air pressure requirements and flow rate (CFM) needs. Light-duty tools: 90–120 PSI Heavy industrial applications: 150–200 PSIHigh-volume systems: 300+ PSIAlways match the compressor's specifications to your equipment's pressure and flow demands to avoid performance loss or energy waste.Compressed Air Energy and Efficiency Plants can reduce energy costs with efficient air compressors. VSD compressors adjust motor speed in response to air demand, saving energy when the system isn't running at full load.You can further improve efficiency by:Installing air leak detection solutions Using proper piping design to reduce pressure dropImplementing compressed air optimization programs Conducting regular industrial compressor maintenance Smart control systems can also monitor compressed air energy consumption and automatically optimize output. Compressed Air Safety TipsSafety is critical to managing industrial air systems. Here are important compressed air safety tips to follow:Never use compressed air for cleaning clothing or skin. Check hoses and fittings regularly for wear, leaks, or cracks.Install safety valves to prevent over-pressurization.Train staff in safe pneumatic tool handling.Ensure proper ventilation to avoid overheating.By maintaining safety standards, you can reduce accidents and extend your compressor's lifespan. Industrial Compressor Brands Comparison It's helpful to consider industrial compressor brands for reliability, energy efficiency, and service when making a choice. Atlas Copco: Known for high efficiency and smart controls. Their compressors integrate intelligent energy management systems that reduce power consumption during low-demand periods. Atlas Copco units are ideal for industries aiming to improve productivity while minimizing operational costs.Ingersoll Rand: Durable models suitable for heavy-duty applications. These compressors are engineered for continuous operation in demanding industrial environments. Ingersoll Rand offers a broad range of air solutions designed to deliver consistent performance and long equipment life.Kaeser: Renowned for quiet operation and advanced monitoring systems. Kaeser compressors use optimized air end designs and precision engineering to enhance efficiency. Their built-in Sigma Control systems ensure reliable, automated performance with minimal downtime. Quincy: Offers reliable rotary screw compressors with low maintenance. Quincy's durable construction and efficient cooling systems make them a trusted choice in manufacturing and processing industries. They provide excellent value through long service intervals and robust performance. Sullair: Focuses on sustainable, energy-efficient compressed air solutions. Sullair compressors are designed with innovative air-end technology to reduce energy use and emissions. Their commitment to green manufacturing makes them a top pick for companies focused on sustainability. Industrial Compressor Sizing Guide Proper sizing ensures consistent air delivery without wasting energy. Follow this industrial compressor sizing guide:Determine total air demand (CFM): Add the flow requirements of all connected equipment.Check peak usage patterns: Select a compressor capable of handling maximum demand.Measure the working pressure (PSI) and match it to your tools' pressure requirements.Factor in future expansion: Plan for at least 20% extra capacity.Include air treatment and storage components, as they affect system pressure and efficiency. Correct sizing not only enhances productivity but also extends equipment lifespan.Industrial Compressor Maintenance Costs Maintenance costs depend on usage, compressor type, and environment. Rotary screw compressors require routine oil and filter changes, while centrifugal compressors demand specialized inspections. Reducing downtime through preventive maintenance keeps your industrial air system efficient. Regular checks on air filters, belts, and valves prevent costly failures and preserve compressed air quality.Industrial Compressor Noise LevelsNoise is often overlooked in industrial compressor selection. Modern rotary screw compressors typically offer low noise levels of 60–75 dB, suitable for indoor installations. Installing soundproof enclosures or isolating the compressor room reduces noise and improves the working environment.Compressed Air Leak Detection Solutions Leaks in your air system can waste up to 30% of the energy in your compressed air. Implementing leak detection solutions, such as ultrasonic sensors or flow monitoring, helps you identify and fix leaks early. Effective leak management enhances the efficiency of industrial air systems and significantly lowers energy bills.Benefits of Compressed Air in Industries The benefits of compressed air in industries extend beyond power supply. It provides:Clean, versatile, and controllable energy Compatibility with pneumatic tools and automated systemsHigh safety compared to electrical powerContinuous operation for heavy machineryFlexibility for diverse industrial environmentsFrom assembly lines to process control, industrial compressed air systems remain the backbone of modern manufacturing.Choosing the Best Industrial Air Compressor When selecting the best for factories, consider these factors: Application needs: Assess whether your operations require constant or variable airflow to ensure the compressor meets peak demand. Choosing the right capacity prevents performance drops and minimizes energy waste during production.Energy efficiency: Select VSD or two-stage compressors to reduce power consumption. Energy-efficient models help lower operational costs and reduce your facility's carbon footprint. Look for systems with energy recovery or smart controls to further enhance performance.Compressor type: Select a rotary screw for continuous operation, a reciprocating screw for intermittent use. Rotary screw compressors are ideal for large-scale manufacturing due to their steady output and durability. Reciprocating models, on the other hand, are more economical for smaller workshops.Noise and location: Evaluate the installation of space and noise-control measures. Consider sound-insulated enclosures or remote placement to maintain a comfortable work environment. Proper ventilation and spacing also help prevent overheating and ensure efficient airflow. Maintenance and service: Check for reliable after-sales support and spare parts availability. Regular maintenance schedules and accessible service kits extend the lifespan of your compressor. Partnering with trusted suppliers ensures minimal downtime and consistent system performance. Evaluating these points ensures the compressor works well in your air system and meets long-term goals.At the Bottom Line Selecting the right industrial air compressor is a strategic investment that influences productivity, efficiency, and operational costs across your facility. Understanding the basics of air compressors, pressure requirements, and energy-efficient compressed air solutions helps you make an informed choice. At eINDUSTRIFY, you can find industrial air compressors and related equipment from trusted and high-quality brands. Whether you need a rotary screw, reciprocating, or centrifugal compressor, our platform ensures reliable options that meet your performance and sustainability needs. Email us at info@eindustrify.com or call us at +1 (888) 774 7632. Register for access to a premium global marketplace.Empower your operations with the right industrial air system, browse, compare, and choose smarter with eINDUSTRIFY.
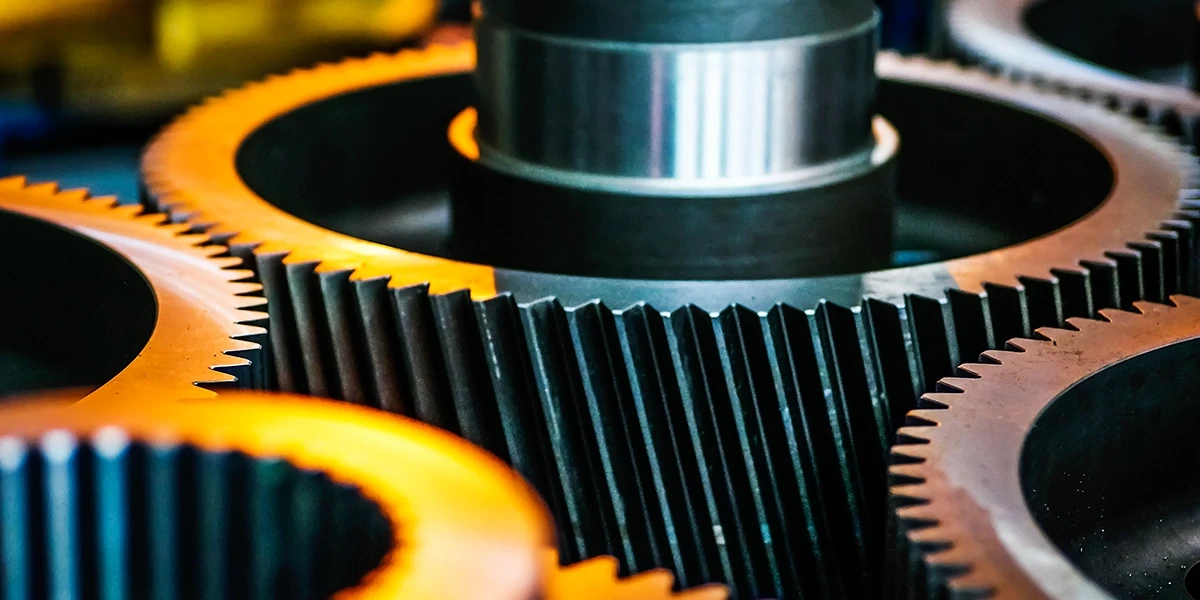

When it comes to power industries, machinery, and even renewable energy systems. Global Power Transmission Equipment plays a pivotal role. These systems facilitate the transfer of energy from one location to another, powering a range of operations from heavy machinery to light industrial applications. Choosing the right power transmission equipment is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency, longevity, and minimal downtime. If you work in energy projects, heavy-duty machinery, or manufacturing, understanding mechanical power transmission components helps you make informed decisions. In this blog, we will discuss everything you need to know about selecting the right power transmission equipment for your needs. With a focus on key elements such as energy transmission systems, high-efficiency power transmission, and durable mechanical accessories. What Is Global Power Transmission Equipment? This refers to the various mechanical components and systems that facilitate the movement of energy from one part of a machine or system to another. This includes components such as belts and chains, couplings and bushings, pulleys and sprockets, bearings, and gear drives. These elements work together to transmit mechanical power from one source (e.g., electric motors) to the components that require it, ensuring that machines operate smoothly and efficiently. Power transmission equipment is used in a wide range of industries, including mining, automotive, renewable energy, and industrial manufacturing. These systems are essential for moving heavy-load transmission parts and heavy-duty machinery to drive components, powering everything from basic machinery to complex energy-sector transmission equipment. Key Components of Power Transmission Equipment To make the right choice, it's important to understand the key components of global power transmission systems. Let's look at some of the most common mechanical power transmission components: Belts and Chains Belts and chains are essential for transmitting power in many industrial applications. Belts are commonly used in systems that require high-efficiency power transmission and where smooth, continuous motion is required. Chains, on the other hand, are more commonly used in heavy-duty systems, where heavy loads are transmitted, such as in mining equipment transmission parts or heavy-duty machinery that drives components. Both belts and chains come in various sizes and designs, depending on the load requirements and operating conditions. The right choice between belts and chains depends on factors like load capacity, speed, and efficiency. Chains are often preferred for applications requiring higher load-bearing capacity and energy transmission systems. Pulleys and Sprockets Pulleys and sprockets are integral parts of mechanical power transmission systems. Pulleys are typically used with belts, and sprockets work with chains. Both help guide the belts and chains, efficiently transmitting energy to the appropriate components. When selecting pulleys and sprockets, consider factors such as material strength, weight, and operating environment. Some applications, such as those in the automotive transmission accessories field, may require smart transmission equipment for improved control and automation. Bearings and Gear Drives Bearings and gear drives ensure that the transmission components can rotate smoothly and without excessive friction. Bearings are often used in systems that involve rotational movement, reducing friction, and wear on the equipment. Gear drives are used to change the speed, torque, and direction of power in a system. Choosing the right bearings and gear drives depends on factors such as load capacity, desired performance, and durability requirements, especially in industries like mining and industrial machinery accessories. Couplings and Bushings Couplings and bushings are used to connect different parts of the transmission system, such as shafts and gear drives, and to prevent misalignment. Couplings play a crucial role in reducing the impact of shock loads and vibrations, especially in heavy-load transmission parts and heavy-duty machinery drive components. Bushings, on the other hand, help reduce friction and wear in rotating parts. Shaft Collars and Clutches Shaft collars and clutches are used to ensure proper shaft alignment and to control the engagement of rotating parts. Shaft collars are designed to hold parts in place along a shaft, while clutches engage or disengage a shaft from a power source. Both components are integral to ensuring the smooth operation of transmission systems, particularly in energy sector transmission equipment and automotive transmission accessories. Factors to Consider: The right power transmission equipment involves considering several factors that will impact your system's performance, efficiency, and durability. Below are key factors to consider: Load Capacity Every application will have different load requirements. Heavy-load transmission parts are often required in industries such as mining, construction, and automotive. It's important to choose equipment that is rated for the maximum load your system will encounter. Heavy-duty machinery drive components and mining equipment transmission parts often need to withstand higher loads, which can require specialized designs. Efficiency and Energy Consumption Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in modern power transmission systems. Whether you're working with high-efficiency power transmission systems or energy transmission systems for renewable energy applications, choosing equipment that minimizes energy waste will help reduce operational costs. Sustainable power transmission materials can also be part of an eco-friendly approach to designing energy systems. Durability and Maintenance For industrial or energy-sector transmission equipment, durability is key. Maintenance-free drive and mechanical accessories reduce the need for frequent repairs and ensure the system remains operational for longer periods. Always choose equipment with a reputation for reliability and longevity to minimize downtime and maintenance costs. Application-Specific Requirements Depending on the industry you work in, you may need specialized OEM transmission accessories, such as those for automotive or mining equipment transmissions. Evaluate the specific needs of your application, including speed, torque, power requirements, and environmental factors, to ensure you select the appropriate components. Sustainability and Environmental Impact With the growing focus on sustainability, it's essential to choose energy-efficient power transmission systems that reduce environmental impact. For renewable energy applications, select equipment made from sustainable materials and components that optimize energy use. Smart transmission equipment can also help reduce emissions and optimize energy use across systems. Applications for Power Transmission Equipment This transmission equipment is used across various industries. Below are some key areas where these components play a vital role: Renewable Energy In renewable energy systems, power transmission components are crucial for efficiently transmitting energy generated from solar, wind, and hydropower sources to the grid. High-efficiency power transmission systems help ensure that energy from renewable sources is delivered without significant loss, supporting sustainable power transmission. Automotive Industry In the automotive sector, transmission systems are vital for transferring power from the engine to the wheel. Components like automotive transmission accessories, pulleys and sprockets, couplings, and bushings are essential for efficient vehicle operation. These components also contribute to the vehicle's overall fuel efficiency and performance. Mining and Heavy Machinery In the mining industry, heavy-duty drive components and transmission parts for mining equipment are crucial for powering excavators, drills, and other heavy equipment. These components need to handle extreme loads and operate efficiently in harsh environments, making durability and performance essential. Industrial Manufacturing Industrial transmission equipment, such as belts and chains, pulleys and sprockets, and shaft collars and clutches, is used in manufacturing plants to power production lines, conveyors, and other machinery. Selecting the right mechanical power transmission components ensures smooth operation and minimizes downtime. At the Bottom Line Good power transmission equipment is critical to ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of your machinery. By considering factors such as load capacity, energy efficiency, durability, and application-specific needs, you can make an informed decision that optimizes your system's performance and reduces long-term costs. Whether you're in the energy, automotive, or industrial manufacturing sectors, partnering with trusted brands and smart transmission equipment ensures you are making a future-proof investment. Partner with eINDUSTRIFY for the right global power transmission equipment At eINDUSTRIFY, we offer a wide range of high-performance power transmission equipment and mechanical power transmission components designed to meet the demands of diverse industries. Explore our products today, and let us help you power your operations with the best industrial machinery accessories, transmission systems, and solutions. Reach out to us at info@eindustrify.com or call +1 (888) 774 7632. Register your account today to access the B2B industrial marketplace.
Industrial automation demands reliable performance, fast response, and precise control. Manufacturers across sectors invest in advanced motion systems because efficient automation drives productivity, reduces downtime, and improves output quality. It plays a vital role in this change. It provides exceptionally responsive motor power. It also offers excellent speed control and steady performance in many different uses. If you plan your next upgrade or want to refine an existing system, you need the right type of motor. Each DC motor option offers unique benefits that support automated workflows, conveyor movement, material handling, packaging, robotics, or assembly operations. This guide looks at the best DC motors for industrial automation. It discusses their strengths and how each option helps your plant's performance goals. Why these Motors Dominate Industrial Automation DC motors power modern automation systems because they offer predictable output and smooth operation. Engineers value their high efficiency, stable speed, torque characteristics, and ease of integration with existing controllers. When processes depend on constant speed under variable load, nothing beats the responsiveness and control of DC motors. Several industries now prioritize DC motors over alternatives because these motors: Deliver fast, dynamic response Support adjustable speed settings Generate high starting torque for accelerated launches Offer simple control through standard drive systems Operate on affordable and scalable DC power sources Plants rely on DC motors because most motors require minimal setup time and integrate seamlessly with automation frameworks. Permanent Magnet DC Motors (PMDC Motors) A Permanent Magnet DC motor provides automation systems with a strong magnetic field without the complexity of external excitation. Engineers prefer PMDC motors for low- to medium-power applications where efficiency and compact size matter. Key Benefits PMDC motors deliver: Consistent torque across a wide range of speeds Strong high starting torque for conveyors, feeders, and pick-and-place units Smooth speed control even at lower RPM High reliability due to fewer components Where PMDC Motors Work Best Automated doors and gates Light-duty robotics Medical automation Packaging lines PMDC motors help businesses simplify automation by providing stable motor power with minimal maintenance. Their direct construction eliminates wound fields, reduces system losses, and supports cost-efficient operation. Brushed DC Motors: Simple, Affordable, and Powerful A Brushed DC Motor is a popular choice in factories. It provides reliable performance with a simple design. The brushes and commutator create the required magnetic field and drive torque with strong responsiveness. Why Engineers Choose Brushed Motors Brushed DC motors offer: Proven reliability in heavy-duty industrial tasks Superior speed torque characteristics Excellent speed control through voltage variation Affordable installation with standard power supply units High motor power output in compact housing Typical Industrial Uses Conveyors Extruders Mixers Indexing systems Brushed motors are suitable for continuous industrial duty, and teams prefer them when they want simple control without complex electronics. Although these motors require brush maintenance, they remain ideal when ruggedness and immediate torque response matter. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC Motors) Brushless DC Motors raise automation performance to new levels by eliminating mechanical brushes and commutators. They use electronic switching to generate rotation, which gives them higher reliability and superior efficiency. Benefits That Matter in Automation BLDC motors deliver: High efficiency for continuous industrial use Outstanding thermal performance Quiet operation with reduced vibration Strong high-power output relative to size Precise adjustable speed operation Where BLDC Motors Excel Automated assembly systems High-precision robotics CNC equipment High-speed fans and pumps BLDC motors help engineers achieve accurate movements in automated machinery. Their electronic control allows optimal speed control and dynamic torque adjustment, making them essential in modern smart factories. Wound Field DC Motors (Shunt, Series, and Compound Types) Industries that need flexible automation rely on wound-field DC motors. These designs provide special performance features. You can choose between shunt, series, or compound configurations depending on your torque and speed requirements. Shunt Wound Motors These motors maintain a steady speed under varying loads. Automation systems that rely on constant speed, like conveyors, use shunt motors. These motors provide stable power output. Series Wound Motors Series motors create immense initial torque. Their strong magnetic field intensifies as the load increases, which helps heavy machinery start under demanding conditions. Compound Wound Motors These motors combine the advantages of both shunt and series designs. Plants select compound motors for equipment that needs high starting torque plus reliable constant speed. How to Choose the Right DC Motor for Automation SystemsSelecting the right DC motor influences workflow efficiency, system longevity, and integration cost. Engineers should evaluate more than just size and ratings. Proper selection ensures optimal motor power and trouble-free performance. Key selection factors are mentioned below: Required Torque Automation lines often shift between light and heavy loads. Choose a motor that maintains smooth speed torque curves during rapid transitions. A well-matched torque profile ensures consistent output and prevents system strain under variable conditions. Speed Range Modern equipment demands adjustable speed capabilities. Choose motors that handle precise speed control through modern drive electronics. This flexibility supports diverse automation tasks and enhances process accuracy. Power Supply Compatibility Verify that the motor is compatible with your existing power supply or DC drive configuration. Incompatible voltages or drive systems can lead to inefficiencies or premature motor failure. Duty Cycle Select motors with thermal ratings that match your operational cycles, especially for continuous industrial automation. Understanding your system's runtime patterns helps prevent overheating and extends the motor's lifespan. Motor Efficiency High-efficiency motors reduce energy costs and heat generation. BLDC and PMDC motors offer excellent performance here. Optimizing efficiency not only cuts operational costs but also supports sustainability goals. Environmental Conditions Harsh environments, such as those found in foundries or chemical plants, require sealed or rugged motor designs to ensure long service life. Choosing motors rated for temperature, dust, and moisture resistance ensures reliable operation in extreme settings. Upgrade Your Automation with the Right DC Motor Industrial automation changes fast. Your systems need reliable DC motors. These motors should provide steady power, accurate control, and long-lasting durability. You can choose from permanent magnet motors, brushed DC motors, brushless DC motors, or advanced wound field designs. Each option can meet your load needs, speed requirements, and automation goals. Partner with eINDUSTRIFY for Reliable DC Motors eINDUSTRIFY supplies high-performance DC motors tailored for every industrial sector. You get access to exceptionally efficient motors. They have strong starting torque and reliable operation for many uses. When you invest in the right motor, you strengthen productivity, enhance machine accuracy, and drive long-term operational success. If you need help choosing the best motor for your system, we will guide you. We will cover specifications, performance data, and integration options. Upgrade your automation today with DC motors that deliver the motor power your plant needs to excel. Please email us at info@eindustrify.com or call us at +1 (888) 774 7632. Register for access to a premium global marketplace.

In every industrial process, precise flow control determines efficiency, safety, and overall performance. One of the most essential components responsible for maintaining this precision is the control valve. From managing pressure and temperature to regulating flow rate, control valves ensure your system runs smoothly within the desired parameters. However, selecting the right control valves for your system isn’t just about picking one off the shelf. It requires understanding your process, the type of control required, and the performance expectations. This blog will help you make an informed decision when choosing the right control valve, ensuring durability, accuracy, and system compatibility. Understanding: A control valve is a final control element in an automated control loop that regulates fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage. In simpler terms, it’s a device that controls the flow rate of liquid, gas, or steam in response to a control signal such as an electrical signal or pneumatic pressure. A typical control valve consists of a valve body, valve stem, actuator, and positioner. When the control system sends a signal (electrical or pneumatic), the valve opens or closes partially, adjusting the flow to match the required set point. This dynamic operation makes control valves indispensable in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and manufacturing. Choosing the Right Valve: Selecting the wrong valve can result in poor control performance, frequent maintenance, and potential safety hazards. The right valve ensures: Accurate flow control and pressure regulation. Energy efficiency through optimized operation. Process stability and consistent output. Reduced wear and downtime, lowering overall maintenance costs. Your choice of types of control valves should depend on the nature of the process of fluid, operating pressure, flow characteristics, and response requirements. Key Factors to Consider: Some of the key factors to choose control valves are listed below. Identify the Type of Control Required The first step is to define what kind of flow control you need, whether it’s throttling, on/off control, or modulating control. On/Off Control: Used when the valve is either fully open or fully closed. Modulating Control: Adjusts flow continuously between minimum and maximum to maintain a set parameter like pressure or temperature. Understanding the type of control helps narrow down which types of control valves suit your system best, such as globe valves, butterfly valves, or gate valves. Consider the Type of Fluid and Flow Characteristics Every process of fluid has unique properties, such as viscosity, corrosiveness, or abrasiveness, that influence valve selection. For example: Globe valves offer precise throttling control for gases and liquids. Butterfly valves are lightweight and ideal for large flow applications. Gate valves are better suited for on/off applications where minimal pressure drop is required. Evaluate how your fluid behaves during flow, laminar or turbulent, and how much pressure drop is acceptable when the valve opens or closes. Choose the Right Actuation Method Control valves operate through different actuation methods, manual, pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric. Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to operate and are widely used due to their reliability and fast response. Electric actuators convert an electrical signal into motion for precise control and easy integration with automation systems. Hydraulic actuators are ideal for high-force applications. Your actuator choice depends on the control system design, available energy source, and safety considerations. Determine Fail-Safe Position Requirements In case of power loss or signal failure, fail-safe positions ensure safety and system integrity. You can choose between: Fail Open: The valve opens to allow flow when a failure occurs, preventing overpressure or overheating. Fail Closed: The valve shuts off the flow to stop the process during an emergency. Your choice depends on the application, whether maintaining flow or stopping it during failure ensures safety. Evaluate the Control Signal and Control Loop Control valves receive control signals from a controller within a control loop. This loop continuously monitors process variables (like flow or pressure) and adjusts the valve position to maintain the desired set point. Pneumatic control signals typically use air pressure (3–15 psi). Electrical signals often operate at 4–20 mA or digital input. Make sure the valves' actuator and positioner are compatible with your system’s control signal type Check Valve Materials and Construction Since the control valve consists of components directly in contact with process fluids, material selection is critical. Common materials include stainless steel, bronze, carbon steel, and specialized alloys. Ensure the materials are corrosion-resistant and suitable for your operating conditions, such as high temperature or pressure. Size the Valve Correctly Improper valve sizing leads to unstable control and inefficiency. A valve that’s too small causes excessive pressure drops, while one that’s too large results in poor control accuracy. Sizing depends on your system’s flow rate, pressure differential, and operating temperature. Use flow coefficients (Cv) and manufacturer data to ensure the valve provides optimal performance throughout its range. Consider Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs While initial cost matters, the total lifecycle cost is more important. Choose valves that are easy to maintain, with readily available parts and service support. Durable designs reduce downtime and operational expenses over time. Common Types & Applications Understanding the major types of control valves helps you match each to its ideal use case: Globe Valve: Excellent for throttling and precise flow control in high-pressure systems. These valves offer accurate modulation of flow and are often used in applications requiring frequent operation. Their design ensures tight shutoff and effective handling of a wide range of fluids, including steam and process liquids. Butterfly Valves: Lightweight, cost-effective, and suitable for large-volume flow applications. They require minimal installation space and provide quick opening or closing action. With options for pneumatic actuators or electric control, they are ideal for systems needing efficient flow management at lower costs. Gate Valve: Best for full open or close operations; not ideal for throttling. The straight-through design minimizes pressure loss when the valve opens fully. Commonly used in pipelines where the valve remains either completely open or closed for long periods, ensuring smooth flow with minimal turbulence. Ball Valve: Provides tight shutoff with minimal pressure loss. The quarter-turn design allows fast operation and reliable sealing against leaks. Ball valves are highly durable and suitable for applications requiring both flow control and isolation, even in high-pressure systems. Diaphragm Valve: Suitable for corrosive or slurry fluids due to their sealed design. The flexible diaphragm isolates the fluid from moving parts, reducing contamination and wear. These valves are widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and water treatment industries for reliable flow control and easy maintenance. Each of these valves can be equipped with pneumatic actuators or electric ones, depending on the required level of automation and control precision. Integrating Control Valves into Your System When integrating a control valve into your system, consider how it fits into the control loop. The valve should react seamlessly to the control signal from the controller, ensuring stable performance and accurate set point maintenance. Automation systems often employ digital communication protocols that enhance feedback and diagnostics, helping detect issues like valve stem friction, actuator lag, or misalignment early. Optimize Your Flow Control with eINDUSTRIFY Choosing the right control valves for your industrial system is crucial to achieving efficient, safe, and reliable operation. From understanding the type of control and actuation method to selecting the appropriate fail-safe mode, every detail matters. At eINDUSTRIFY, we connect you with top-quality control valves and components designed to meet diverse industry demands. Whether you need globe valves, butterfly valves, or custom-engineered solutions, our platform offers trusted brands and expert support to help you make the right choice. Email us at info@eindustrify.com or call us at +1 (888) 774 7632. Register for access to a premium global marketplace. Explore our range of high-performance control valves today empowering your system with precision, durability, and control that drives productivity.
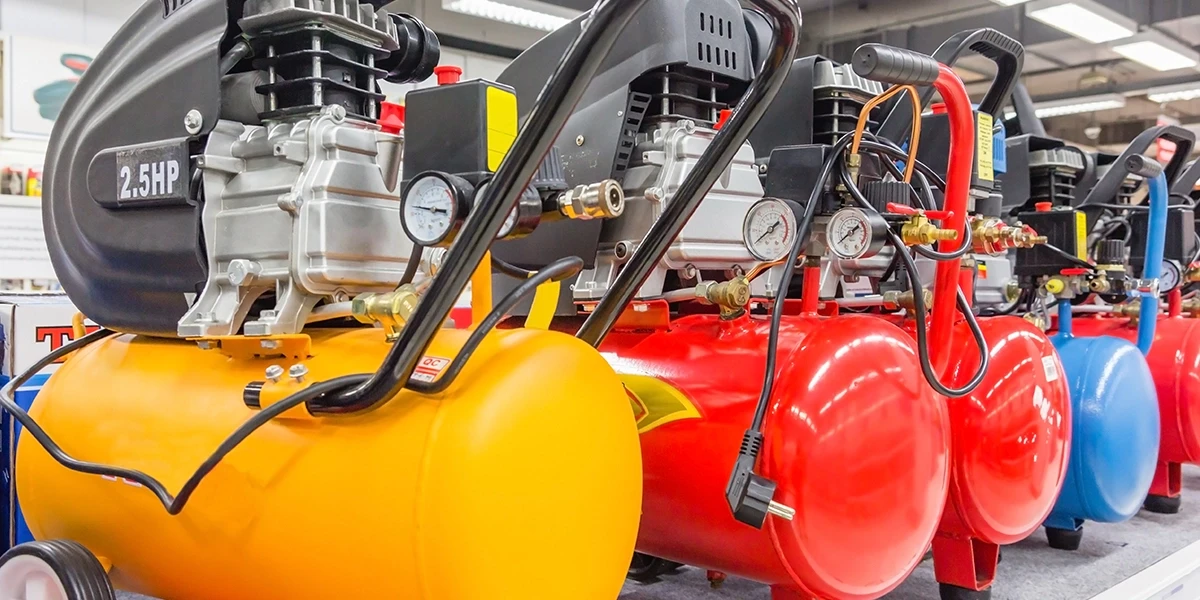

Compressed air powers industrial tools, assembly lines, and heavy equipment reliably. Factories and workshops use air compressors to work efficiently, keep machines running smoothly, and reduce downtime. Use this guide to compare models, brands, and features and find the air compressor that fits your needs. Industrial Air Compressor:An industrial air compressor converts power from an electric motor or engine into compressed air energy. This compressed air powers pneumatic tools, manufacturing lines, spray painting systems, and automated machinery. Industrial air systems run continuously, handle high pressure, and maintain a steady flow, unlike residential compressors. They supply energy to everything from automotive assembly plants to food processing facilities. Knowing air compressor basics helps you set up an efficient plant air system. It provides the right air pressure for industrial use. Working:Compressed air acts as a form of stored energy. An industrial air compressor pulls in air and squeezes it to increase its pressure. Once released, this pressurized air performs mechanical work, powering drills, conveyors, or paint sprayers. In industrial air systems, air flows through pipes, tanks, and devices like dryers and filters before reaching the machines. Clean, dry, and stable air ensures both system longevity and operational reliability. Types: When selecting the best industrial air compressor for factories, it’s crucial to understand the different types available. Each compressor has unique performance characteristics, maintenance requirements, and cost implications. Rotary Screw Compressors: A rotary screw compressor is one of the most popular choices for continuous operation. It uses two interlocking helical rotors to compress air efficiently. Ideal for 24/7 manufacturing operations Delivers consistent pressure and flow rate Works quietly and requires minimal maintenance These are preferred in industrial air applications such as automotive manufacturing, chemical processing, and food packaging. Reciprocating (Piston) Compressors: A reciprocating compressor uses pistons to compress air inside cylinders. Best for intermittent use or smaller operations Generates higher pressures but with more noise Requires more maintenance due to moving parts Rotary screw compressors are more energy-efficient and good for continuous use. Reciprocating compressors is better for occasional high-pressure tasks. Centrifugal Compressors: These large-scale compressors use high-speed impellers to transfer energy into the air. Suited for massive industrial plants High flow capacity with steady pressure Low oil carryover for clean air applications Centrifugal systems are often used in refineries, steel production, and power generation facilities. Scroll and Vane Compressors: Compact and reliable, these types are common in labs, electronics, and medical industries. They operate quietly and deliver oil-free air, ideal for sensitive environments. Brand Comparison: When searching for air compressors, brand selection plays a key role. Top brands like Atlas Copco, Ingersoll Rand, Kaeser, Gardner Denver, and Quincy are reliable, energy-efficient, and well-supported. Atlas Copco: Atlas Copco sets the benchmark for innovation in energy-efficient compressed air solutions. Its VSD compressors change motor speed to match air demand, saving energy and lowering costs. Ingersoll Rand: Ingersoll Rand compressors offer rugged designs suitable for harsh environments and flexible air system components. Built for durability and performance, these compressors deliver reliable compressed air even in demanding industrial conditions. Their advanced engineering ensures efficiency, longevity, and easy integration into existing industrial air systems. Kaeser Compressors: Kaeser Compressors combine German engineering precision with advanced technology to deliver exceptional performance and reliability. Their smart control systems optimize compressed air energy use, enhancing industrial air system efficiency while maintaining quiet operation. Gardner Denver: Gardner Denver makes industrial air compressors that cut downtime and lower operating costs. Their focus on low maintenance costs and energy-efficient designs helps facilities achieve consistent output with less intervention. Quincy Compressor: Quincy Compressor stands out for its flexible range of customizable compressor configurations designed to meet specific plant requirements. The brand’s strong warranty coverage and proven engineering give operators confidence in long-term reliability. Chicago Pneumatic Reciprocating Air Compressor: The Chicago Pneumatic Reciprocating Air Compressor provides powerful and efficient compressed air solutions for various industrial applications. It is built to be durable and high-performing, ideal for tough environments and continuous use. Champion Centurion II Series The Champion Centurion II Series is a high-efficiency air compressor designed for reliable performance in industrial applications. It features advanced engineering and durable components. It ensures a long-lasting service life. It makes it ideal for heavy-duty. Always check industrial compressors for noise, horsepower (HP), flow rate (CFM), and the pressure (PSI) your operation needs. Size Guide Before investing, assess your plant’s compressed air system design carefully. Selecting the wrong size affects efficiency, pressure stability, and energy costs. Key sizing factors include: Air Demand: Calculating total air demand is the foundation of proper compressor sizing. Add the CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) requirements for all connected tools, equipment, and machinery operating simultaneously. Include peak usage periods when multiple systems run at once. Pressure Range: Your air pressure requirements for industrial use determine how much PSI your compressor must deliver. Most pneumatic tools and air systems work best at 90–120 PSI, though some equipment may need higher pressure. Duty Cycle: The duty cycle shows how long a compressor can run. Rotary screw compressors run all day, while reciprocating ones suit light use. Future Growth: Industrial operations evolve, and so should your air system design. Always plan for future growth by including a 20–30% capacity buffer when sizing your compressor. Expansion could involve adding production lines, pneumatic tools, or automation systems that increase air demand. Right sizing your compressor ensures optimal industrial air system efficiency and prevents unnecessary energy waste. Energy-Efficient Air Compressors for Plants: Energy accounts for nearly 70% of a compressor’s lifetime operating cost. Investing energy-efficient air compressors helps reduce overall power consumption and carbon footprint. Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Compressors VSD compressors automatically adjust motor speed to match air demand. This feature significantly lowers compressed air energy costs and reduces wear on components. Air Treatment Equipment Dryers, filters, and regulators keep air clean and moisture-free, extending equipment life and reducing downtime. Compressed Air Leak Detection Solutions Even a small leak can waste up to 30% of compressed air. Regular leak detection and repair save energy and boost air system efficiency. Compressed Air Optimization Real-time monitoring and smart controllers find problems and keep your air system running efficiently. Air System Components and Design An efficient air system includes more than just the compressor. Key air system components include: Compressor unit: The compressor is the heart of every industrial air system, producing and supplying air to all connected equipment. Its performance determines the overall efficiency, reliability, and output of the system. Air dryer: An air dryer removes moisture from compressed air to prevent rust, corrosion, and damage to downstream equipment. Dry air improves tool performance and extends the life of pneumatic systems. Filters: Filters play a critical role in protecting your industrial compressed air system by capturing oil, dust, and particulate contaminants. Clean filtration ensures better air quality, reduces maintenance needs, and prevents premature equipment failure. Storage tank: The storage tank acts as a buffer, providing stable air pressure and reducing frequent compressor cycling. It stores excess compressed air during low-demand periods and supplies it when demand peaks. Distribution piping: Distribution piping delivers compressed air from the storage tank to tools, machines, and workstations throughout the facility. Efficient piping design minimizes pressure drops, air leaks, and energy loss. Using good materials and a proper layout keeps airflow smooth and equipment running well. A well-planned compressed air system design ensures balanced airflow, minimal pressure drop, and maximum productivity. Benefits: Below are some of the key benefits of compressed air in the industries listed below. Versatility: The right industrial air compressor lets plants run many machines at once, keeping production flexible. This versatility allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing production needs, making compressed air systems essential for maximizing uptime and operational efficiency. Safety: By using industrial air systems, facilities reduce dependency on electrical wiring near hazardous materials, ensuring a safer workspace. Additionally, air tools generate less heat and sparks, minimizing fire hazards. Efficiency: An industrial air compressor delivers reliable, steady power that keeps production moving without fluctuations. It delivers steady torque and pressure, keeping pneumatic tools, automation systems, and heavy equipment running smoothly under continuous use. Scalability: One of the most valuable advantages of an industrial air compressor system is its scalability. As your business grows, your compressed air system can expand easily without redesigning your facility. Clean Energy: Modern industrial air compressors play a vital role in advancing sustainability by reducing energy consumption and emissions. Through energy-efficient compressed air solutions, industries can cut their carbon footprint while maintaining high productivity. These benefits make compressed air the lifeblood of modern industrial production. Air Pressure and Flow Considerations Every industrial air compressor must meet the system’s CFM and PSI demands. CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) measures airflow; higher CFM supports multiple tools simultaneously. PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) measures pressure, critical for powering pneumatic machinery effectively. Balancing flow rate (CFM) and pressure (PSI) ensure each process receives adequate energy without overloading the system. Safety Tips: Safe compressed air handling is essential for both workers and equipment. Never point air hoses toward people. Use approved fittings and hoses rated for the system’s PSI. Drain moisture traps regularly to prevent corrosion. Conduct periodic safety training and maintenance checks. Follow manufacturer guidelines for industrial compressor maintenance costs and service intervals. A safe, well-maintained system prevents accidents and extends equipment life. Reducing Noise Levels Noise can impact productivity and worker safety. Choose compressors with sound-insulated enclosures, anti-vibration mounts, and efficient cooling systems. Rotary screw compressors generally run quieter than reciprocating models, making them ideal for indoor environments. Energy-Efficient Solutions To enhance industrial air system efficiency, consider these strategies: Optimize compressor placement and ventilation. Maintain proper piping size to reduce pressure drops. Recover waste heat from compressors for space heating or water preheating. Schedule off-peak operations to reduce energy demand. Install automatic shutdown systems for idle periods. Sustainable practices like these improve overall compressed air optimization and reduce total cost of ownership. Choosing the Best Compressor When evaluating air compressors for sale, prioritize: Energy efficiency and VSD technology Durability and brand reputation Compressor horsepower (hp) suited to workload After-sales service and availability of spare parts Scalability for future expansion Each factor contributes to long-term reliability and lower operational expenses. At eINDUSTRIFY, you can compare multiple industrial compressor brands and find the model that aligns with your production goals. Maintenance and Costs: Regular maintenance ensures your industrial compressed air systems deliver consistent performance. Inspect filters, belts, and oil levels weekly. Schedule quarterly vibration and temperature checks. Replace worn parts promptly to prevent breakdowns. Review annual energy audits to identify optimization opportunities. Proactive maintenance reduces industrial compressor maintenance costs and improves uptime. The Future: Modern plants are adopting smart compressed air systems with IoT-enabled monitoring and AI-driven analytics. These innovations enhance industrial air system efficiency, automate maintenance scheduling, and optimize energy usage. As global sustainability goals rise, energy-efficient air compressors will help plants cut emissions and boost profits. At the Bottom Line: Choosing the right industrial air compressor is more than buying equipment. It is an investment in efficiency. It improves productivity and saves energy. Understanding how compressed air works helps you choose the right system. Compare rotary screw and reciprocating compressors. Plan your system properly. This builds a reliable air system for your facility. At eINDUSTRIFY you can compare compressors for sale. You can check the top brands and find energy saving solutions that fit your plant. Equip your business with the best, because efficient compressed air means powerful performance. Email us at info@eindustrify.com or call +1 888 774 7632 to register for access to a premium global marketplace.
Power transmission is important in industrial work. Most machines use it. It moves power and motion. It supports car assembly lines, mining machines, and energy systems. Industries need strong and reliable parts. These parts help machines run smoothly. The right accessories improve reliability. They reduce downtime and increase safety. This blog explains key power transmission accessories. It describes their functions. It also helps you choose the best parts for industrial drive systems. What Are Power Transmission Accessories? Power transmission accessories are supporting components that help a drive or motion system work efficiently. They protect and enhance main parts like gears, motors, and shafts. Common accessories include bearings, gear drives, couplings, bushings, fasteners, shaft collars, clutches, pulleys, and sprockets. These industrial machinery accessories keep machines running smoothly by maintaining alignment, absorbing shocks, reducing friction, and transmitting power efficiently under stress. Key Categories: Power transmission accessories are essential for modern industrial and energy sector equipment. They keep machines running efficiently, reduce wear, and ensure safety. Here are the main types and their roles: Timing Belts & Roller Chains Timing belts keep shafts synchronized, which is critical in automotive systems and high-speed machinery. Roller chains, used with sprockets, handle heavy loads and are common in conveyor systems for mining and manufacturing. Proper tension and material choice make these accessories low-maintenance and long-lasting. Pulleys and Sprockets Pulleys and sprockets transfer motion from belts and chains. They control speed, torque, and gear ratios. In heavy machinery and energy systems, durable pulleys and sprockets help reduce slippage, vibration, and wear. Bearings and Gear Drives Bearings Support rotating shafts and reduce friction, ensuring smooth and efficient motion. Types include roller, thrust, and spherical bearings. Gear drives (spur, helical, bevel, worm, planetary) adjust speed, torque, and direction. High-quality bearings and gear drives prevent failures in high-stress applications. Couplings and Bushings Couplings connect shafts while absorbing vibration and allowing slight misalignment. Bushings protect shafts and provide smooth motion with less maintenance. These accessories safeguard machines against sudden torque spikes, misalignment, or thermal expansion. Shaft Collars and Clutches Shaft collars hold components in place along a shaft. Clutches control engagement or disengagement of drive systems. They are critical for safe operation of conveyors, automotive systems, and industrial machines. Fasteners for Transmission Systems Fasteners include bolts, nuts, keys, pins, springs, and set screws. They keep components securely in place under heavy loads. Choosing high-strength and corrosion-resistant fasteners ensures reliability, especially in mining, offshore, and energy applications Specialized Applications: Heavy Duty, Energy & Mining Power transmission in industries like mining, oil & gas, renewable energy, and heavy manufacturing requires strong and specialized accessories to handle tough conditions.Heavy machinery needs parts that can withstand high torque, shock loads, and abrasive environments. These components must support heavy loads reliably. Mining equipment requires accessories that resist dust, moisture, chemicals, and vibration. Heavy-duty bearings and vibration-resistant components are essential for smooth operation. Energy systems, including wind turbines, hydroelectric, and thermal plants, need accessories that are durable yet lightweight and corrosion resistant. Examples include pulleys and belts for cooling systems, gear drives in turbines, and clutches in grid tie systems. Mechanical Power Transmission Equipment Global Market Size The mechanical power transmission equipment market is projected to grow from $66.1 billion in 2024 to $70.31 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 6.4%. This growth is driven by rising industrialization, automotive sector expansion, globalized supply chains, increased manufacturing automation, and growing demand for agricultural machinery. Benefits of High-Quality Accessories Investing in well-designed power transmission components and industrial drive accessories offers several key benefits: Higher overall equipment efficiency results in less energy wasted due to friction or misalignment. Longer equipment life due to reduced wear and better load distribution. Reduced maintenance costs thanks to maintenance of free drive accessories or parts that require minimal lubrication. Improved uptime and fewer breakdowns, resulting in increased ROI and throughput. Enhanced safety: accessories such as clutches, couplings, and properly designed bearings can prevent catastrophic failures. Choosing the Right Power Transmission Accessories Selecting the correct set of accessories involves striking a balance between performance, cost, and environmental impact. Here are the key factors to guide specifications. Load Type & Magnitude Distinguish static loads vs dynamic loads. Heavy-load transmission parts require bearings with high load capacity, resilient roller chains, heavy-duty pulleys, and robust fasteners. Speed & Precision Needs Use timing belts for accuracy, silent or helical gears for smooth motion, and pick belts or chains based on noise and precision. Environment & Conditions Exposure to dust, moisture, chemicals, and temperature extremes demands sealed, corrosion resistant materials. Use bushings, bearings, and chains with sealing, lubrication, or material coatings that are suitable for harsh environments. These are found in mining or offshore energy applications. Durability & Maintenance Profile For hard-to-reach places, use maintenance-free parts like sealed bearings, self-lubricating bushings, or strong belts to need less care. OEM & Spare Compatibility Ensure accessories match OEM standards for safety, quality, and fitness. Shaft collars, couplings, clutches, and fasteners should conform to correct dimensions and tolerances for replacements or upgrades. Sustainability & Materials Select sustainable power transmission materials where possible recycled metals, materials with long lifespan, low energy fabrication to meet environmental goals. The energy sector and modern industrial drive systems increasingly require these. Real-World Examples and Use Cases Different industries rely on customized power transmission accessories to ensure smooth, efficient, and reliable operations. Automotive Manufacturing: In automotive assembly lines, accessories like timing belts, clutches, couplings, and bushings ensure smooth and predictable motion. Robots and conveyor systems depend on low-friction bearings and durable fasteners that withstand vibration. Mining & Cement Plants: Mining and cement operations use conveyor belts, heavy-duty roller chains, large sprockets, sealed bearings, and robust gear drives. These accessories handle continuous heavy loads and dusty environments, reducing downtime and improving efficiency Power Generation (Wind, Hydro, Thermal): In power plants and turbines, large gearboxes rely on precision gear drives and high-strength bearings for optimal performance. Fans, pumps, and other systems use pulleys, belts, and rust-proof fasteners that need little or no maintenance. Material Handling & Manufacturing: Conveyors, packaging lines, presses, and CNC machines need accessories that deliver precise, high-efficiency power transmission with minimal wear. Timing belts ensure synchronous operations; gear drives manage torque, and couplings absorb misalignments for smoother motion. Trends & Innovations in Power Transmission Accessories Industries are now pushing for more innovative, more sustainable, and higher-performance accessories. Smart Transmission Equipment: Sensors embedded in bearings or couplings can monitor temperature, vibration, and misalignment in real time. These accessories feed into dashboards that alert maintenance teams before a failure occurs. High efficiency Power Transmission: Materials, surface treatments, and advanced design minimize energy loss to friction or heat. For example, precision-machined gear teeth, low-friction coatings on bushings, and optimized chain profiles. Maintenance free & Self-lubricating Accessories: Bearings or bushings with sealed grease packs or composite materials eliminate the need for frequent relubrication. Ideal for remote installations or high-risk environments. Sustainable Materials & Green Manufacturing: Use recycled materials, eco-friendly coatings, and long-lasting parts to reduce the environmental impact of mechanical transmission accessories. Avoiding Common Problems and How Accessories Help Many downtime issues trace back to poor selection, improper installation, or neglect of power transmission accessories. Here are typical problems and how good accessories mitigate them: Problem Cause Accessory Focused Solution Belt slip or failure Misaligned pulleys, wrong belt type Use timing belts or V belts sized properly; use pulleys with correct groove shape Chain wear and elongation Poor lubrication, wrong material Use roller chains designed for heavy loads; regularly lubricate; utilize hardened or coated sprockets Shaft misalignment Rigid mounting, thermal expansion Flexible couplings, bushings; use shaft collars to locate parts correctly Bearing overheat & failure Friction, contamination Use sealed or shielded bearings; select high precision gear drives; ensure proper lubrication Fastener fatigue or loosening Vibration, dynamic loads Use high tensile fasteners; locking or vibration resistant bolts; periodic checks Tips for Installation & Maintenance Even the best accessories fail if installers ignore details. Follow these tips: Align pulleys, sprockets, and shafts precisely. Small misalignments increase wear dramatically. Tension belts and chains are correct. Under tension chains skip; over tension damages bearings. Lubricate bearings and gear drives at recommended intervals. Use the correct type of grease or oil. Monitor vibration and temperature on bearings, couplings, and clutches to ensure optimal performance. Use sensors if possible (innovative equipment). Replace fasteners periodically, especially in high vibration contexts. Use locking hardware. Bottom Line Power transmission accessories are critical to the performance, safety, and longevity of industrial systems. Timing belts, bearings, couplings, and fasteners all help machines run smoothly and reliably. By selecting high-quality, application-specific accessories and maintaining them properly, industries can reduce downtime, improve energy efficiency, and support sustainable operations. Final Thoughts:eINDUSTRIFY is a B2B platform for industrial drive systems. We provide parts like timing belts, roller chains, bearings, gear drives, couplings, bushings, shaft collars, clutches, and fasteners. We partner with OEMs and quality manufacturers, ensuring that products meet international standards. Email us at info@eindustrify.com or call us at +1 (888) 774 7632. Register for access to a premium global marketplace.

Industrial automation thrives on accurate, responsive sensing. Today’s manufacturing plants, assembly lines, and warehouses rely heavily on industrial sensors to monitor variables, control processes, and ensure safety. Training your systems to communicate through sensors radically transforms output, quality, and cost efficiency. Here, we explore the types of industrial sensors that lead to the automation revolution. Integrate this knowledge into your automation strategy to elevate performance, and enjoy seamless, optimized operations. Types of Industrial Sensors to Boost Automation Different industrial sensors—like proximity, temperature, and pressure sensors—are very important because they help improve automation. Each type serves as a specific function, from detecting objects and measuring force to monitoring environmental conditions for optimal performance. Let’s break down key sensor categories: Proximity Sensors & Photoelectric SensorsProximity Sensors Determine the presence or absence of objects without physical contact. A conveyor might use them to detect metal parts approaching machinery. Photoelectric Sensors use light beams to detect objects. They shine a light, sense of reflection, and trigger actions, excellent for fast-moving lines. Together, they enable seamless object detection in automation systems. Motion SensorMotion Sensors track movement, vital for robotics or safety zones. They detect unintended motion, helping systems stop or slow machinery. They also support safety systems by promptly alerting control units when someone enters hazardous zones. Level SensorsLevel Sensors track liquids or solids, think of fluid levels in tanks or grain in silos. They prevent overflows, asset damage, and production delays by triggering alarms or control actions when levels cross threshold. Pressure Sensors Pressure Sensors Monitor fluid or gas pressure, vital for hydraulic or pneumatic systems. They help maintain stable operations, avoid leaks, and optimize energy use. They feed Predictive Maintenance systems that spot pressure drops before breakdowns. Temperature Sensors & Humidity SensorsTemperature Sensors Track heat levels in processes, ovens, or motors. They optimize thermal control, prevent overheating, and ensure product quality. Humidity Sensors monitor moisture. Manufacturers use them in dry room environments or processes sensitive to moisture levels. Both sensors protect quality and prevent spoilage or defects. Force Sensors Force Sensors measure push or pull, critical in packaging, pressing, or assembly. They ensure the production line applies consistent force, protecting components and optimizing energy use. How Sensors Drive Automation Benefits Sensors drive automation by continuously collecting real-time data to monitor and control processes with precision. They help improve efficiency, enable predictive maintenance, and ensure consistent product quality across industrial systems.Enhance Quality Control Sensors detect defects or anomalies early. Photoelectric or proximity sensors identify missing parts; temperature and humidity sensors catch deviations from ideal conditions. Force sensors ensure consistent assembly pressure. These sensors help maintain high quality control standards and reduce rework or waste. Enable Predictive Maintenance Predictive Maintenance depends on continuous monitoring. Pressure, temperature, and vibration data (via motion sensors) alert teams before failures occur. You prevent costly downtime and extend machinery life. Improve Safety SystemsPutting sensors in place safeguards workers and equipment. Motion sensors, proximity sensors, and photoelectric sensors act as eyes and guards, detecting human presence and triggering emergency stops. They support robust safety systems that comply with industry standards. Streamline Operations with Electrical Signal FlowSensors convert physical phenomena into electrical signals. Systems interpret that information and act—whether adjusting pressure, switching valves, or halting conveyors. By managing electrical signal flow, sensors form the backbone of responsive automation networks.Safety Systems Powered by SensorsAutomation menaces involve machines, humans, and materials. Build safety systems using sensors like proximity, photoelectric, or motion detectors. They halt machinery when staff enter danger zones or if parts veer of course. Use redundant sensors or multi-modal detection to strengthen safeguards. When your safety network triggers fast, you prevent accidents, and shield both people and production.Choosing the Right Type of Sensor Choosing the right sensor depends on your needs. Consider the environment it will be used in. Think about how accurate it must be. Also, consider how fast it should respond. When you select sensors, consider these factors: Detecting the Presence: Choose proximity or photoelectric sensors when you need to spot objects without contact reliably. Environmental Conditions: Use temperature, humidity, or pressure sensors when you face extremes or require precise control. Required Accuracy: Force sensors and level sensors provide excellent precision when exact measurement matters. Response Time: Photoelectric sensors respond quickly, perfect for highspeed lines. Some force or pressure sensors act slower but deliver high accuracy. Maintenance Needs: opt for durable sensors for harsh environments. Contactless sensors like photoelectric or capacitive proximity sensors reduce wear and tear.Integration and Wiring: Ensure sensors support your automation protocol and wiring (analog, digital, industrial field bus). Good Electrical Signal Flow simplifies integration and data collection. Related: What Are Industrial Controls? A Guide for BuyersIndustrial Manufacturing Trends & Sensor Roles In today's industrial world, automation is at the center of everything. Companies use connected sensors to move toward Industry 4.0. These smart sensors help run production lines, robots, and control systems. Many manufacturers place sensors in their machines. This helps them make quick decisions, from the factory floor to the cloud.Bottom Line:Sensors used for predictive maintenance make this change possible. They constantly measure vibration, temperature, pressure, flow, or force. With the help of analytics, these readings show patterns that can predict equipment problems before they happen. This reduces emergency repairs and keeps machines in good condition. This proactive method cuts downtime and lowers maintenance costs.Trust eINDUSTRIFY to keep your systems running smoothly with dependable isolation and expert support. Kindly email us at info@eindustrify.com or call us at +1 (888) 774 7632. Register for access to a premium global marketplace.
B2B eCommerce platform designed specifically for industrial businesses